Publicado
Leptodactylus vastus (LEPTODACTYLIDAE) predation on an endemic frog, and a compilation of its diet
Depredación de Leptodactylus vastus (Leptodactylidae) en una rana endémica y una recopilación de su dieta
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v27n1.90678Palabras clave:
Batrachophagy, Chapada Diamantina, Literature review, Caatinga, Northeastern Pepper Frog (en)Batracófago, Chapada Diamantina, Revisión de literatura, Caatinga, Rana Pimienta del Noreste (es)
Descargas
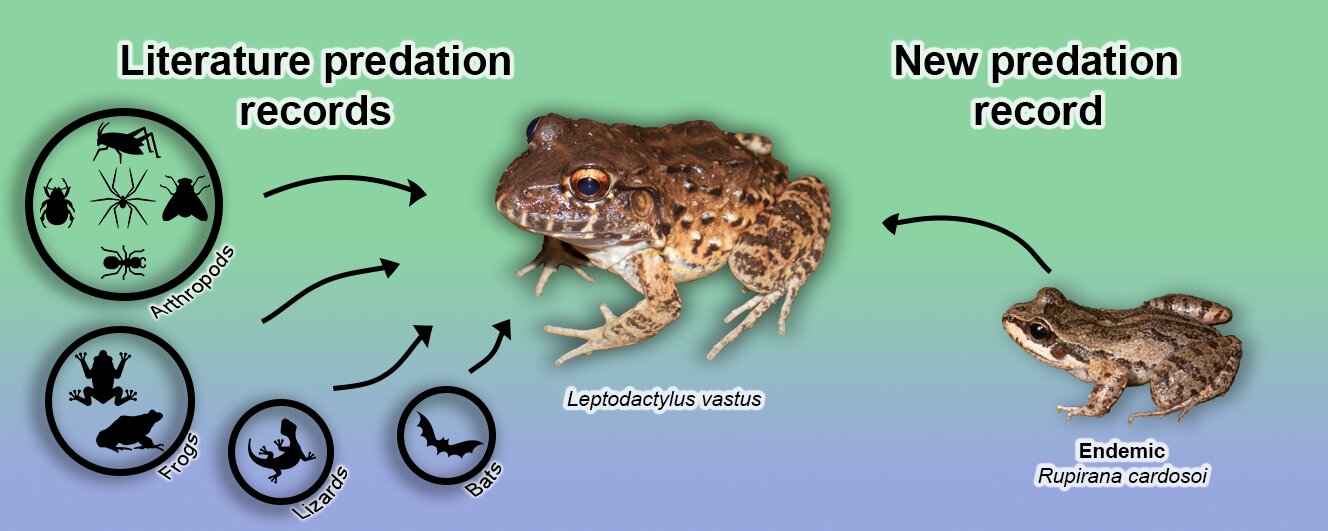
Diet composition constitutes basic information on the natural history of the species. Despite the amount of data acquired in the last years, much remains to be known specially for geographically widespread species. Here we compiled the available dietary items of Leptodactylus vastus and report the first predation event upon Rupirana cardosoi by a juvenile L. vastus. The fact these species are syntopic in the region probably resulted in this novel predation event. Different from previous L. vastus predation observations, the specimens we observed do not present a striking difference in body size, but L. vastus was able to almost swallow L. cardosoi, coherent with findings that mouth size is related to prey selection in anurans. Also, our literature review showed that L. vastus is a generalist and opportunistic predator, that prey upon small vertebrates (Amphibia, Squamata, and Mammalia).
La composición de la dieta constituye información básica sobre la historia natural de la especie. A pesar de la cantidad de datos adquiridos en los últimos años, aún queda mucho por conocer, especialmente para especies geográficamente extendidas. Aquí compilamos los elementos dietéticos disponibles de Leptodactylus vastus y reportamos el primer evento de depredación de Rupirana cardosoi por un juvenil de L. vastus. El hecho de que estas especies sean sintópicas en la región probablemente resultó en este nuevo evento de depredación. A diferencia de las observaciones previas de depredación de L. vastus, los especímenes que observamos no presentan una diferencia notable en el tamaño corporal, pero L. vastus fue capaz de casi tragar R. cardosoi, en coherencia con los hallazgos de que el tamaño de la boca está relacionado con la selección de presas en los anuros. Además, nuestra revisión de la literatura mostró que L. vastus es un depredador generalista y oportunista, que se alimenta de pequeños vertebrados (Amphibia, Squamata y Mammalia).
Referencias
Caldas, F. L. S., Garda, A. A., Cavalcanti, L. B. Q., Leite-Filho, E., Faria, R.G., and Mesquita, D. O. (2019). Spatial and trophic structure of anuran assemblages in environments with different seasonal regimes in the Brazilian Northeast region. Copeia, 107(3), 567-584. https://doi.org/10.1643/CH-18-109 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1643/CH-18-109
Ceron, K., Oliveira-Santos, L. G. R., Souza, C. S., Mesquita, D. O., Caldas, F. L. S., Araujo, A. C., and Santana, D. J. (2019). Global patterns in anuran–prey networks: structure mediated by latitude. Oikos, 128(11), 1537-1548. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.06621 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.06621
Coco, L., Borges Júnior, V. N. T., Fusinatto, L. A., Kiefer, M. C., Oliveira, J. C. F., Araujo, P. G., Costa, B. M., Van Sluys, M., y Rocha, C. F. D. (2014). Feeding habits of the leaf litter frog Haddadus binotatus (Anura, Craugastoridae) from two Atlantic Forest areas in southeastern Brazil. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 86(1), 239-249. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0001-37652014113012 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-37652014113012
Davis, N. E., Forsyth, D. M., Triggs, B., Pascoe, C., Benshemesh, J., Robley, A., Lawrence, J., Ritchie, E. G., Nimmo, D. G., and Lumsden, L. F. (2015). Interspecific and geographic variation in the diets of sympatric carnivores: Dingoes/Wild Dogs and Red Foxes in South-Eastern. Plos One, 10(6), e0120975. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120975 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120975
de Sá, R. O., Grant, T., Camargo, A., Heyer, W. R., Ponssa, M. L., and Stanley, E. (2014). Systematics of the Neotropical genus Leptodactylus Fitzinger, 1826 (Anura: Leptodactylidae): phylogeny, the relevance of non-molecular evidence, and species accounts. South American Journal of Herpetology, 9(s1). https://doi.org/10.2994/SAJH-D-13-00022.1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2994/SAJH-D-13-00022.1
Gouveia, S. F., Rocha, P. A., Mikalauskas, J. S., and Silveira, V. V. Rhinella jimi (Cururu Toad) and Leptodactylus vastus (Northeastern Pepper Frog) Predation on bats. Herpetological Review, 40, 210.
Guimarães, F. P. B. B., Marques, R., y Tinôco, M. S. (2015). Leptodactylus vastus (Northeastern Pepper Frog) Cannibalism. Herpetological Review, 46, 74-75.
Haddad, C. F. B., Toledo, L. F., Prado, C. P. A., Loebmann, D., Guasparini, J. L., and Sazima, I. (2013) Guia dos Anfíbios da Mata Atlântica - Diversidade e Biologia (1ª ed). Anolis Book Editora.
Heyer, W. R. (2005). Variation and taxonomic clarification of the large species of the Leptodactylus pentadactylus species group (Amphibia: Leptodactylidae) from middle America, northern South America, and Amazonia. Arquivos De Zoologia, 37(3), 269-348. https://doi.org/10.11606/issn.2176-7793.v37i3p269-348 DOI: https://doi.org/10.11606/issn.2176-7793.v37i3p269-348
Jansen, M., and Schulze, A. (2012). Molecular, morphology and bioacoustic data suggest Bolivian distribution of a large species of the Leptodactylus pentadactylus group (Amphibia: Anura: Leptodactylidae). Zootaxa, 3307(1), 35-47. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3307.1.2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3307.1.2
Acuña Juncá, F., and Lugli, L. (2009). Reproductive biology, vocalizations, and tadpole morphology of Rupirana cardosoi, an anuran with uncertain affinities. South American Journal of Herpetology, 4(2), 173-178. https://doi.org/10.2994/057.004.0208 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2994/057.004.0208
Juncá, F., and Silvano, D. (21 de April de 2020). Rupirana cardosoi. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2004.RLTS.T57322A11620407.en DOI: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2004.RLTS.T57322A11620407.en
Leite Filho, E., Feijó, A., and Rocha, P. A. (2014). Opportunistic predation on bats trapped in mist nets by Leptodactylus vastus (Anura: Leptodactylidae). Biotemas, 27(3), 205-208. https://doi.org/10.5007/2175-7925.2014v27n3p205 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5007/2175-7925.2014v27n3p205
Santana, D. O., Rocha, S. M., Silva, I. R. S., and Faria, R. G. (2012). Predation of Leptodactylus latrans (Anura, Leptodactylidae) and Hypsiboas albomarginatus (Anura, Hylidae) by Leptodactylus vastus (Anura, Leptodactylidae) in north-eastern Brazil. Herpetology Notes, 5, 449-450.
Santos Neto, A. G., Barbosa, L. P., Santos, D. P., and Santos-Silva, C. R. (2015). Predation on Hypsiboas faber (Anura: Hylidae) by Leptodactylus vastus in a temporary pond in the Atlantic Forest at Capela, Sergipe. Natureza on line, 13(3), 126-127.
dos Santos, E. M. (2009). Notas sobre predação de anuros em uma poça temporária no nordeste do Brasil. Boletim do Museu de Biologia Mello Leitão, 25, 77-82.
Teles, D. A., Rodrigues, J. K., and Teixeira, A. A. M. (2015). Leptodactylus vastus (Northeastern Pepper Frog). Diet. Herpetological Review, 46, 75.
Teles, D. A., Teixeira, A. A. M., Araujo Filho, J. A., and Sousa, G. G. (2017). Leptodactylus vastus (Northeastern Pepper Frog). Diet. Herpetological ReviewHerpetol, 48, 410.
Toledo, L. F., Ribeiro, R. S., and Haddad, C. F. B. (2007). Anurans as prey: an exploratory analysis and size relationships between predators and their prey. Journal of Zoology, 271(2), 170-177. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00195.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00195.x
Cómo citar
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Descargar cita
CrossRef Cited-by
1. Mario Alberto Morales-Collazos, Luis Enrique Vera-Pérez. (2023). DEPREDACIÓN DE LA RANA ENANA DE PETERS Engystomops petersi POR LA RANA TERRESTRE GIGANTE Leptodactylus pentadactylus (ANURA: LEPTODACTYLIDAE) EN EL PIEDEMONTE AMAZÓNICO COLOMBIANO. Revista Latinoamericana de Herpetología, 6(2) https://doi.org/10.22201/fc.25942158e.2023.2.639.
Dimensions
PlumX
Visitas a la página del resumen del artículo
Descargas
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2021 Acta Biológica Colombiana

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
1. La aceptación de manuscritos por parte de la revista implicará, además de su edición electrónica de acceso abierto bajo licencia Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 (CC BY NC SA), la inclusión y difusión del texto completo a través del repositorio institucional de la Universidad Nacional de Colombia y en todas aquellas bases de datos especializadas que el editor considere adecuadas para su indización con miras a incrementar la visibilidad de la revista.
2. Acta Biológica Colombiana permite a los autores archivar, descargar y compartir, la versión final publicada, así como las versiones pre-print y post-print incluyendo un encabezado con la referencia bibliográfica del articulo publicado.
3. Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
4. Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos institucionales, en su página web o en redes sociales cientificas como Academia, Researchgate; Mendelay) lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).