Prospección de lectinas en especies de Labiadas colombianas. Un
enfoque sistemático-ecológico - III. Principalmente especies
exóticas cultivadas o naturalizadas
JOSÉ LUIS FERNÁNDEZ-ALONSO
NOHORA VEGA
GERARDO PÉREZ
Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Apartado
7495, Bogotá D.C., Colombia. jlfernandeza@unal.edu.co
Real Jardín Botánico CSIC, Plaza de Murillo 2, 28014 Madrid, España,
jlfernandeza@rjb.csic.es
Chemistry Department, Biochemistry Laboratory, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá. Colombia. navegac@unal.edu.co; jrperezg@unal.edu.co
ABSTRACT
This is the third study of lectin and mucilage detection in Labiatae nutlets from Colombia. It was carried out on 30 taxa; 15 of them belonging to 14 genera in which no previous studies have been carried out in this field, the other 15 belonging to previously studied genera. A differential response was observed in the group of genera and species studied in terms of mucilage presence as well as lectin activity which consistently increased after extract treatment with Pectinex. Lectin activity was detected in 26 species, being important (more than 60% activity) in at least 75% of them. Genera such as Aegiphila, Agastache, Ballota, Mentha and Origanum, whilst not presenting mucilage, did present lectin activity, with high activity in most cases. This is the first time that a lectin has been reported in these genera. Salvia (in all but Salvia sections studied) presented mucilage and important lectin activity.
Key words. Labiatae, lectin, mucilage, Agastache, Hyptis, Ocimum, Salvia, Stachys.
RESUMEN
Este es el tercer estudio sobre detección de mucílagos y lectinas en núculas de Labiadas de Colombia. Fue llevado a cabo en 30 taxones, 15 de ellos pertenecientes a 14 géneros que no contaban con estudios previos en este campo y los otros 15 pertenecientes a géneros que ya contaban con alguna especie estudiada. Se observó una respuesta diferencial en el grupo de géneros y especies estudiados en lo que a presencia de mucílago y a actividad de lectina se refiere, actividad que se vió consistentemente incrementada con el tratamiento de los extractos con Pectinex. Se detectó actividad de lectina en 26 especies, y actividad importante (superior al 60% de actividad) en al menos el 75% de ellas. Los géneros Aegiphila, Agastache, Ballota, Mentha y Origanum, no presentaron mucílago y su actividad de lectina fue alta en la mayoría de los casos. Se registra actividad de lectina en estos géneros por primera vez. Salvia (en todas las secciones estudiadas a la fecha) presentó mucílago e importante actividad de lectina.
Palabras clave. Labiatae, lectina, mucilago, Agastache, Hyptis, Ocimum, Salvia, Stachys.
Recibido: 14/05/2009
Aceptado: 23/09/2009
INTRODUCTION
The Labiatae family which according to current circumscription also groups
several genera previously located in the Verbenaceae family (Cantino 1992a,
1992b, Wagstaff et al. 1998, Harley et al. 2004, Atkins 2004), is represented
in Colombia by a total of 41 genera and ca. 308 species according to the latest
work (Fernández-Alonso 2003, 2006, Pérez et al. 2006, Fernández-Alonso
2008a, 2008b). Colombia has 32 genera and 228 taxa (sp., subsp. and var.) from
the traditionally recognized Labiatae, only a small part (17 spp.) consisting
of foreign plants which have become naturalised to form an integral part of
Colombian flora (Table 1), and
also another 22 species from foreign Labiatae widely grown in Colombia for their
various uses (Fernández-Alonso et al. 2003, Fernández-Alonso &
Rivera 2006). The 9 new -Verbenaceae- genera, which are now dealt within the
Labiatae, have a total of 80 native or naturalised species in Colombia (López-Palacios
1977, 1986, Rueda 1992, Aymard 2005, this work) and prospecting work in this
particular area has just begun.
Continuing with prospecting of mucilages and lectins in the Labiatae family,
focused on previous work carried out on Colombia native species (Fernández-Alonso
et al. 2003, Pérez et al. 2006), the third contribution towards this
ongoing work has resulted in cataloguing 24 non-native Colombian species belonging
to 17 genera. As follows: a) 6 species currently naturalised in Colombia belonging
to the Leonurus L., Ocimum L., Salvia L., Solenostemon Tonn. and Stachys L.,
b) 13 species which are frequently cultivated in Colombia, belonging to Agastache
Clayton ex Gronov., Hyssopus L., Lavandula L., Melissa L., Mentha L., Ocimum
L., Origanum L., Rosmarinus L., Salvia L., Satureja L. and Thymus L. and c)
5 exotic species (from the Iberian peninsula), non cultivated in Colombia, belonging
to Ballota L., Sideritis L. and sections Aethiopis, Plethiosphace of Salvia
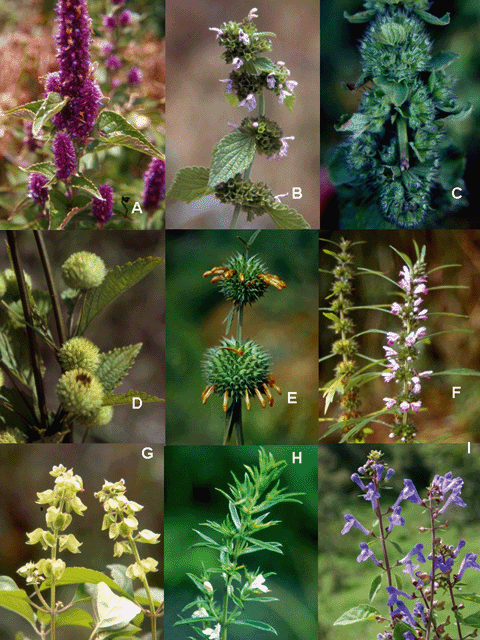
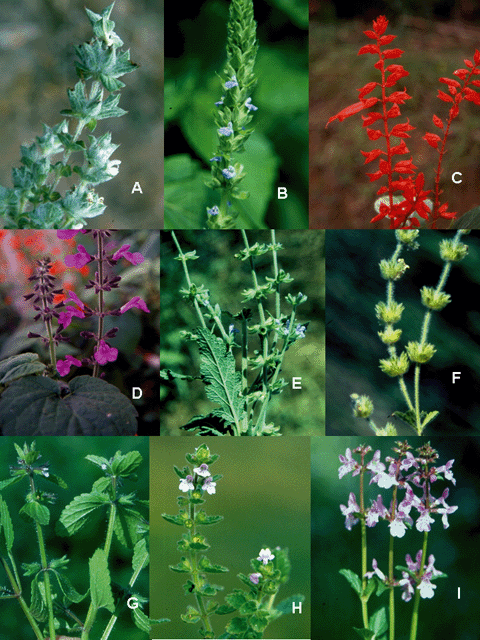
L. (Table 2 and Figure
1 and Figure 2). Other 14 accessions of native species
came from (belonging to the Aegiphila Jacq., Hyptis Jacq., Ocimum, Salvia, Scutellaria
L. and Stachys) are also studied.

This combination let us extend our analysis of mucilages and lectins to a considerable number of species (112 accessions, belonging to 90 taxa) where these compounds have not been described before and also provided additional confirmatory evidence regarding genera studied in previous work (Fernández-Alonso et al. 2003, Pérez et al. 2006).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collecting and preserving botanical samples and fruits
The same procedures described by Fernández-Alonso et al. (2003) and Pérez
et al. (2006) have generally been followed in that referring to collection itineraries
and dates, herbarium sample-taking protocols, collecting nutlets and live material
for culturing.
Itineraries. The plants included in this study came from different itineraries
mainly carried out on the eastern cordillera of Colombia, where 14 accessions
of native species came from (belonging to Aegiphila Jacq., Hyptis Jacq., Ocimum,
Salvia, Scutellaria L. and Stachys) and 6 from naturalised exotic species, belonging
to Leonurus L., Leonotis R. Br., Ocimum, Salvia and Stachys (Figure
1 and Figure 2). The exotic species which are only
found as cultivated plants in Colombia for their medicinal, culinary or ornamental
uses represent another important group; 13 species belonging to Agastache, Hysoppus,
Lavandula, Melissa, Mentha, Ocimum, Origanum, Rosmarinus, Salvia, Satureja and
Thymus were analyzed. Five exotic wild species of Ballota, Salvia and Sideritis
from central Iberian Peninsula fields of thyme (-tomillares-) were also studied
(Appendix 1 and Figure 1 and Figure
2).
Samples: The following specimens were collected in all cases:
a) Collecting fruit (nutlets) for erythroagglutination and enzyme-linked lectinosorbent
assays (ELLSA) and mucilage;
b) Collecting herbarium control samples (about 180 collections) which were included
as vouchers (Appendix 1) and nutlet samples for the project's sample file (currently
containing 150 accessions); and
c) Collecting live samples for culturing and follow-up in Bogotá's Botanical
Gardens, where around 50 taxa are being cultured. Control material, as well
as fruit samples, were catalogued and deposited in the Colombian National Herbarium
(COL) and many of these samples have been duplicated in the HUA, FMB, JBB, MEDEL
herbaria, abbreviated according to Holmgren et al. (1990).
Seeds produced by an hybrid originated in culture conditions (S. x tunica-mariae
Fern. Alonso) were studied so that the results obtained with this plant could
be compared to those from parental species.
A Labiatae nutlet reference collection has also been established with more than
480 accessions, some being stored in the nutlet/seed library in the Colombian
National Herbarium and others in Bogotá's Botanical Garden's seed bank.
Types of growth and types of habitat in those taxa studied
All taxa studied have been catalogued according to habit type (growth type)
and habitat (altitude at which taxa are found) to enable correlating these parameters
with information resulting from mucilage and lectin assays. The biological/ecological
function of mucilage is still not clear (even though various hypotheses have
been suggested related to different aspects regarding germination) and no correlation
has been established between the presence of mucilage and determined environmental
conditions. Detailed classical types of habit (shrubs, subshrubs, scandent shrubs
and perennial herbaceous and annual or biannual herbs) and habitat (tropical,
subAndean, Andean and paramo) have been considered and described in previous
work (Fernández-Alonso et al. 2003). The Tree biotype (Tr) has been added
to the foregoing, being present in Aegiphila cuatrecasana Moldenke; regarding
the types of habitat where samples came from, the following have been included
for exotic species which are not present in Colombia: those having Mediterranean
origin (E-Medit), subtropical origin (E-Subtr) and those having a Tropical origin
(E-Tro), (Table 3).
Two variants having general characteristics (humid or dry) have been considered
for each altitude range according to the amount of rainfall, delimiting dry
areas as being those having a rainfall of less than 800-1,500 mm/year, depending
on altitude. When a plant lives in more than one altitude range its least habitual
altitude is given in parentheses.
Lectin extraction
Extraction was done with 20 mM phosphate buffer- 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.2-7.4 (PBS)
in 1:10 (w/v) or 1:20 (w/v) ratio if a viscous solution appeared, seeds being
left to soak in the solution for 2-3 h, at 4ºC; they were then macerated
and shaken at 4ºC, for 16 h. The extract was spun at 39,000xg for 15 min
at 4ºC. The supernatant was used immediately or treated with Pectinex.
Pectinex treatment
Supernatant pH was adjusted to pH 4.7 with concentrated AcOH; 28 µl Pectinex
Ultra SP-L (Novo) was then added per ml of extract. This was incubated at 28ºC
for 4 h, being occasionally shaken. The pH was adjusted to 7.0 with diluted
NaOH and lectin activity was determined.
Lectin detection and quantification assays
Two assays were done to assess lectin presence:
a) Erythroagglutination. The assays were done on human RBCs as described (Pérez
1984) and on T/Tn-exposed RBCs. A+ human RBCs were enzymatically treated to
expose T or Tn determinants (Hirohashi et al. 1985). Crude extracts were used
in all cases. If appropriate, the haemoagglutination titre was determined and
expressed as being the highest dilution where agglutination was still observed.
b) Lectin was also detected by ELLSA, according to the procedure described by
Vega & Pérez (2006) for crude extracts treated with Pectinex and
left un-treated. The plates were sensitized with asialo ovine submaxillary mucin
(aOSM) isolate, using biotinylated Vicia villosa isolectin B4 as control (Tn
antigen specific) and streptavidin peroxidase as detection system.
Mucilage assay
The mucilage assay was performed using fresh nutlets, following Hedge's recommendations
(1970). A minimum 4-hour period was established for hydration (distilled water).
Even though slight differences were detected in mucilage colour and degree of
transparency, mucilage quantity was evaluated in terms of the following ratio:
width of mucilage halo/seed width (smaller diameter), observed values varying
between 0 and 3. Basic mucilage characteristics regarding colour, consistency
and general appearance followed Hedge's terminology (1970).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
I- MUCILAGE PRESENCE
Macroscopic differences were observed amongst the taxa in which mucilage formation was presented in terms of their appearance, based on colour, consistency and degree of transparency; they could be grouped into four morphological types according to their characteristics which, in some ways, could be variations of the four basic ones (milky white-opaque, brown-opaque, translucent and transparent) recognized for species of Salvia by Hedge (1970). Thus, as this was not the object of the present work, information referring to the anatomical or micromorphological characterisation of types of mucilage in Labiatae has not been included, an aspect which has been treated for some taxa by authors such as Grubert (1974) or Martín-Mosquero et al. (2004). The four basic types are listed below, indicating in which species studied they have been observed. These morphological types are schematically represented (Figure 3), showing a possible relationship between them.

Type 1: - Transparent and fibreless or having radiating cordons (Figure 3-1), embraced by the mass of mucilage, having an egg-white aspect. This is only present in the four genera from tribe Mentheae (Nepetoideae): Melissa, Rosmarinus, Salvia (S. amethystina J.E. Sm. subsp. amethystina and S. hispanica L.) and Thymus and a Hyptis species (tribe Ocimeae): H. pectinata (L.) Poit.
Type 2: - Transparent, irregularly fragmented and having conical processes (detached from the nutlet) embraced by the mass of mucilage (Figure 3-2): Only observed in Nepetoideae, Ocimeae, in one species of Ocimum (O. gratissimum L.). This deals with a very distinctive type of nucula, due to the tuberculate ornament which it presents.
Type 3A: - Milky white/pale, having flexuous fibres in the mass of mucilage (Figure 3-3): Nepetoideae were present in both representatives of tribe Ocimeae: Hyptis (H. suaveolens (L.) Poit. var. mollisima Fern. Alonso) and Mentheae: Salvia (S. coccinea Ettling., S. horminium L. and S. splendens Sellow ex Roem. & Schult.). The cordons gave a "cottony" aspect to the mass of mucilage.
Type 3B: - Transparent-Milky white/pale. Mucilage having two concentric layers (a transparent external one and milky white/pale internal one) with flexuous fibres in a mass of mucilage (Figure 3-4). It represents just one variant of type 3. It has only been observed in Salvia verbenaca L., (Nepetoideae, Mentheae).
Type 4: - Milky white/pale with fibres or radiating cordons embraced by the mass of mucilage, forming a rigid mass in most cases (Figure 3-6). It is present in Mentheae (Nepetoideae): Ocimum (O. basilicum L.., O. campechianum Mill.) and Salvia (S. aethiopis L., S. aratocensis (Wood & Harley) Fern. Alonso, S. sphaceliodes Benth., S. x tunica-mariae). Cordons are less notable in S. aratocensis and S. sphaceliodes (Figure 3-5) and have a less consistent aspect.
There are ten genera within the group of taxa studied in which the formation of a mucilaginous mass due to moistening has not been observed (Agastache, Ballota, Leonurus, Leonotis, Hyssopus, Lavandula, Mentha, Origanum, Satureja and Sideritis), partially agreeing with the consulted literature (Grubert 1974, Ryding 1992a, Budantsev & Lobova 1997, Ryding 2001, Martín-Mosquero et al. 2005). It was also presented in a species belonging to Hyptis (H. capitata Jacq.) and in two belonging to Salvia (S. lavandulifolia Vahl. and S. officinalis L.), which will be mentioned later on.
The Lamioideae, Scutellarioideae and Teucrioideae subfamilies
Concerning the species included within the subfamily Lamioideae, the results (Table 3) may be generalised as follows.
Traces (0.2) of mucilage were only observed in one species of Stachys (S. micheliana
Briq. ex Mich.) of six studied, two in this work and four in previous work (Fernández-Alonso
et al. 2003, Pérez et al. 2006). The absence of mucilage in this genus
seems to be characteristic, bearing in mind that Ryding (1992a) obtained negative
results in 7 species of Stachys. Other species from the Lamiodeae subfamily
also did not present mucilage (Table
3), thereby corroborating and adding to Ryding's results (1992a) where myxocarpy
was not detected in 4 species of Ballota, 2 from Leonotis, 2 from Leonurus,
7 from Stachys and 4 from Sideritis; the reports to date indicate that the absence
of mucilage in nultles is generalised in this subfamily.
The absence of mucilage in nultles has been confirmed for Aegiphila (subfamily
Teucrioideae), having two species studied (Pérez et al. 2006, this work),
and Scutellaria (subfamily Scutellariodeae), having four species studied (Pérez
et al. 2006, this work). Nevertheless, dealing with both cases of large genera
(Harley et al. 2004), a greater number of species needs to be examined for having
a more complete panorama concerning the occurrence of myxocarpy in them.
The Nepetoideae subfamily
On the contrary, most species analyzed in the Nepetoideae subfamily in this
work presented myxocarpy, being extremely common in Hyptis and Ocimum (Table
4). These results agree with those described by Ryding (1992a) who found
mucilage in 16 of 22 species of Hyptis, including H. pectinata and H. suaveolens.
It is worth noting the absence of myxocarpy in H. capitata, corroborating Ryding
report (1992a). The scarce amount of mucilage in Ocimum gratissimum, a species
from Africa, is also worth noting (Table
4) when contrasting results obtained by ourselves in this work on other
species of Ocimum: O. basilicum and O. campechianum, in previous work (Pérez
et al. 2006) and in those described by Grubert (1974) and Ryding (1992b), who
detected mucilage in 17 Ocimum taxa.
Within tribe Mentheae (subfam Nepetoideae), myxocarpy is habitual in genera such as Salvia and in the species analyzed from Melissa, Rosmarinus and Thymus (M. officinalis L., R. officinalis L. and T. vulgaris). On the contrary, it is absent in species belonging to Agastache, Hysoppus, Mentha, Origanum and Satureja (Table 4). In the case of Hyssopus officinalis L., where we did not observe mucilage, there is contradictory evidence in the literature, as Ryding (1992a) did not observe mucilage whilst Grubert (1974) included this specie as having myxocarpy. The absence of mucilage in Mentha spicata indicates that there are species with and without mucilage within this genus, as Grubert (1974) found myxocarpy in seven species of Mentha, without analysing M spicata L., whilst Ryding (1992a) cited (without specifying them) that some species of Mentha and Origanum are lacking mucilage.
The data compiled by Grubert (1974) revealed the presence of myxocarpy in 5 species of Satureja and in 20 species of Thymus whilst we did not observe mucilage in Satureja montana and a scant amount in Thymus vulgaris (0.5). It is worth specifying that the data of Grubert (1974) and Ryding (1992a, 1992b) are qualitative as, contrasting with this work, these authors did not evaluate the relative abundance of mucilage according to that proposed by Hedge (1970). It seems then that in the case of Hyssopus, Mentha and Satureja there may or may not appear mucilage, depending on the species. The results of myxocarpy in Melissa officinalis agreed with Grubert (1974) and those for Rosmarinus officinalis agreed with that found by Ryding (1992a) and Grubert (1974).
Of the Salvia species analyzed in this work only S. lavandulifolia and S. officinalis, belonging to Salvia subgenus and both having large seeds, did not present mucilage and in the rest of the species this was evident (0.7-3.0). It is worth pointing out that of the 40 species studied in this work and in our previous reports (Fernández-Alonso et al., 2003, Pérez et al. 2006), 37 have mucilage without seeming to have a correlation with the type of habitat where they come from. Qualitative detection of myxocarpy in several species of Salvia studied here (S. aethiopis, S. coccinea, S. hispanica, S. horminum, S. splendens and S. verbenaca) is mentioned by Grubert (1974) and Oran (1997) in the case of S. verbenaca. We only found different results in the case of S. officinalis, a specie in which we did not observe mucilage presence. It should be stressed that no mucilage was also present in S. lavandulifolia, a specie which is taxonomically very close to S. officinalis (Figuerola et al. 1990), recently treated as being a subspecies of S. officinalis (Reales et al. 2004) and which had not any previous reports. The generalised occurrence of myxocarpy in the Salvia genus has been pointed out by Grubert (1974) who detected it in 90 species, by Hedge (1970) who only found three lacking mucilage after testing 40 Asian species, and by Oran (1997) who found it in 12 species which had not been previously examined by prior authors.
II- LECTIN PRESENCE
IIA- ELLSA ASSAYS
Contrasting with that described in the literature for myxocarpy where a very
considerable number of genera has been examined, the evidence concerning the
presence of lectins in Labiatae until a few years ago was fundamentally limited
to species native to species of Salvia natives of the Old World. The available
information came from the reports of Bird & Wingham (1974, 1976, 1977, 1982)
and in isolated contributions regarding Hyptis suaveolens (Bird 1960), Salvia
horminum (Moore & Marsh 1975) and Moluccella laevis L. (Bird & Wingham
1969). A systematic study has recently been started regarding the presence of
lectins in neotropical Labiatae (Fernández-Alonso et al. 2003, Pérez
et al. 2006) where the presence of lectins has been detected in a considerable
number of species belonging to different genera. The results presented below
are part of this study.
A1- The Teucrioideae, Scutellarioideae and Lamioideae subfamilies (Aegiphila,
Scutellaria, Ballota, Leonurus, Leonotis, Sideritis and Stachys)
Lectin directed against Tn antigen was detected for the first time in species
belonging to Ballota, Leonurus, Leonotis and Sideritis (Table
4), considerably broadening the number of Labiatae where lectins are found.
Due to the availability of material restricting analysis to just one species
from each of these genera, other species must be assayed for discerning how
generalised the presence of lectin is in them. Species where the presence of
lectin have been established come from geographically very different localities
and they are not taxonomically close within the subfamily (Iwarsson & Harvey
2003, Harley et al. 2004).
The experimental evidence indicates that ELLSA assay sensitivity and treating extracts with Pectinex facilitates the detection of these proteins. In the case of Aegiphila cuatrecasana, the level of lectin detected was similar with and without Pectinex treatment, compared to that observed with Aegiphila bogotensis (Spreng.) Moldenke (Pérez et al. 2006) where the effect of Pectinex treatment is evident, allowing greater lectin activity to be detected. It is worth stressing this result since it deals with taxonomically close species (Lopez-Palacios 1977, 1986). Something similar has been observed with five of the six species of Stachys studied (this work, Fernández Alonso et al. 2003, Pérez et al. 2006); however, lectin was never detected in the case of S. pusilla (Well.) Briq. The available data for Scutellaria (this work, Pérez et al. 2006) has shown great variability regarding the presence/absence of lectin, as two out of the four species did not present lectin. It would be recommendable to continue prospecting with other species from this genus given the presence of several taxa from this genus in Colombia (Fernández-Alonso, 2005).
A2- Tribes Lavandulae and Ocimeae from the Nepetoideae subfamily (Lavandula,
Hyptis, Ocimum and Solenostemon)
Appreciable lectin activity was observed in Ocimum after digestion with Pectinex
in two of the three species analyzed (Table
4), thereby confirming a previous report (Pérez et al. 2006) indicative
of the presence of lectins able to recognise Tn antigen, this being corroborated
by positive erythroagglutination assay results (Table
5).
The Hyptis species analyzed here had absence of lectin, even following treatment with Pectinex, except in Hyptis pectinata which showed activity (even though being relatively low). Similar lectin activity was observed (Fernández-Alonso et al. 2003) in a sample of H. pectinata from another locality, suggesting that there is a small amount of lectin in this specie. Nevertheless, the information about the presence of lectins in species belonging to this genus (Fernández-Alonso et al. 2003, Pérez et al. 2006), present very variable results regarding lectin activity, even within the same specie, as in the case of H. capitata samples coming from three different localities.
The other specie analyzed within the Ocimeae, Solenostemon scutellariodes (L.)
Codd., an ornamental exotic species cultivated around the world, presented high
lectin activity (70.8%), being the first report concerning the presence of lectins
in this genus. This genus, which is widely diversified in tropical areas of
the Old World (Suddée et al. 2004), seems to offer good prospects for
prospecting for this type of protein.
Regarding tribe Lavandulae, lectin has been detected in Lavandula vera having
considerable activity, this is the first report concerning the presence of lectin
in this economically important genus having predominantly Mediterranean and
subtropical distribution in the Old World (Upson 1997).
A3- Nepetoideae subfamily, tribe Mentheae (Agastache, Hysoppus, Melissa, Mentha,
Origanum, Rosmarinus, Salvia, Satureja and Thymus.)
Within the species corresponding to the Nepetoideae subfamily, tribe Mentheae,
lectin presence is very frequent, particularly in that referring to the Salvia
genus (Table 4) where only four
of the eleven species analyzed in this work did not show the presence of lectin.
Similar results were obtained by Bird & Wingham (1974, 1976, 1977) who did
not detect lectin in 12 out of 36 species analyzed. The presence of lectins
in S. aethiopis, S. horminum and S. verbenaca detected by Bird & Wingham
(1974, 1976) was quantitatively confirmed by ELLSA assay (Table
5).
Similarly to that found in previous work (Fernández-Alonso et al. 2003,
Pérez et al. 2006), the effect of Pectinex treatment in species from
the Nepetoideae subfamily is notorious, thereby allowing the ELLSA assay to
be used for detecting high lectin activity in species which otherwise would
have been classified as lacking: it wich is the case of Melissa officinalis,
Origanum vulgare, Salvia amethystyna subp amethystyna, S. x tunica-mariae and
S. sphaceloides subsp. pax-fluminensis. Something similar happens in S. hispanica,
S officinalis and S. splendens which had previously shown the absence of lectin
with the erythroagglutination assay (Bird & Wingham 1974, 1976), in contrast
to that observed by ourselves. A careful review of the pertinent literature
showed that for all the taxa included in Table
4 this is the first time that the presence of lectin has been described
in Agastache, Hysoppus, Melissa, Mentha, Origanum, Rosmarinus, Satureja and
Thymus. On the other hand, information regarding Salvia has added 8 extra taxa,
belonging to diverse infrageneric categories, some exclusive to the Old World.
It is worth noting that cultivated species of Labiatae and thus having easily
accessible nultles would not have been analyzed within the set of systematic
investigations carried out during the 1970s by several groups in Europe or North-America
(Bird & Wingham 1974, 1976, 1977, 1982, Moore & Marsh 1975).
IIB- ERYTHROAGGLUTINATION ASSAYS
The erythroagglutination results (Table
5) showed that all the Salvia species analyzed agglutinated Tn antigen-carrying
erythrocytes, with the exception of S. officinalis, S. melaleuca Epling and
S. sphaceloides sub pax-fluminensis. An important number of species recognized
A- or T-determinants, frequently having lesser titres, meaning that one must
be very careful when defining anti-Tn specificity; the presence of A1 antigen-specific
lectin in Hyptis suaveolens var. mollissima Alonso described for the first time
by Moore & Marsh (1975) is interesting in this context and this has been
confirmed in the present work. Comparing these results with those obtained by
ELLSA assay (Table 3 and Table
4) it was observed that the presence of Tn antigen-recognising lectins could
be detected in all species. However, the activity obtained with S. officinalis
was not very high following Pectinex treatment, thereby explaining the negative
erythroagglutination result since this is a less sensitive method.
A recent review of lectins present in the Labiatae family (Pérez & Vega 2007) synthesised the results obtained by other investigators regarding the presence of lectins in some of the species studied in this work. The available data indicates that it was not possible to detect the presence of these proteins through erythroagglutination assays on crude seed extracts of these species (Bird & Wingham 1974, 1976, 1977, 1982). This discrepancy is explainable if one considers that pectins interfering with detecting lectins were not eliminated in such work and that erythroagglutination is notoriously less sensitive than the ELLSA assay.
FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
The advantage of using a semi-quantitative method for evaluating myxocarpy (basically following Hedge's (1970) criteria) lies in the fact that it is relatively easy to use a stereoscope for discerning different morphological types of mucilage based on their external appearance, consistency and halo size. We have stressed (based on that described in this work) the absence of mucilage in Salvia officinalis and S. lavandulifolia, differently to that which occurs with most Salvia species genus. Ryding's findings (1992a) were confirmed for the first species and such absence was also detected for the first time in the second, both forming a complex of very related Mediterranean taxa.
The results obtained in this and previous work (Fernández-Alonso et al. 2003, Pérez et al. 2006) have shown that lectin detection assay sensitivity becomes conspicuously increased if extracts have been previously treated with polygalacturonases (Pectinex) which digest the pectins (the main component of mucilage). This point is important as mucilage is abundant in many Labiatae species (particularly those belonging to the Nepetoideae subfamily). Using the ELLSA assay for detecting lectins instead of erythroagglutination offers greater sensitivity since it allows lower amounts of lectin to be observed at the same time as supplying semi-quantitative data about a protein's relative abundance. On the other hand, erythroagglutination using enzymatically treated erythrocytes (or untreated ones) leads to discriminating lectin specificity regarding T and Tn antigens and those antigens responsible for blood groups.
An additional question is raised regarding lectins' possible physiological role given that within a particular genus such as Salvia, where an important number of taxa have been analyzed (44), lectin is absent in around 10% of them. This could indicate that lectins are not an essential constituent in the seed or that they are replaced by protein having different specificity.
Considering the high number of existing Labiatae species and diversity and broad distribution of some of the larger genera, such as Aegiphila, Clerodendrum, Hyptis, Ocimum, Plectranthus, Salvia, Scutellaria and Stachys (Table 1), then it is evident that additional systematic prospecting work is required for having a broader panorama about the presence of mucilage and lectin in the nultles of different species. This will contribute towards understanding the functional and ecological significance of these compounds and also lead to extending the possibilities of using species from this family which have numerous types of economically important secondary metabolites, such as essential oils, antioxidant pigments, flavonoides and terpens.
ACKOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the Universidad Nacional de Colombia (DIB) and COLCIENCIAS for financing this project's fieldwork and laboratory work. We would also like to thank the Universidad Nacional's Chemistry Department and the Institute of Natural Sciences for the facilities provided for carrying out the present study, and Carlos Aedo from the Royal Botanical Garden in Madrid (MA) for his collaboration in obtaining the literature. We thank Ramón Morales (MA) and two anonymous reviewers for the critical review of the manuscript.
LITERATURE CITED
1. ATKINS, S. 2004. Verbenaceae pp. 449-468, in: J.W. Kaldereit (ed.). Flowering
Plants. Dicotyledons Lamiales (except Acanthaceae incluiding Avicenniaceae).
The Families and genera of Vascular Plants VII. Spring Verlag, Berlin.
2. AYMARD, G.A. 2005. Verbenaceae. pp. 407-445, in: P.E. Berry, K. Yatskievych
& B.K. Holst (eds.) Flora of the Venezuelan Guayana 9. Rutaceae-Zygophyllaceae.
Missouri Botanical Garden Press. St. Louis, Missouri.
3. BIRD, G.W.G. 1960. Anti-A agglutinins from the seeds of Hyptis suaveolens
Poit. Brit. J. Haematol 6: 151-153.
4. BIRD, G.W.G. & J. WINGHAM. 1969. Anti-N from Moluccella laevis. Experientia
25: 1091.
5. BIRD, G.W.G. & J. WINGHAM. 1974. Hemagglutinins from Salvia. Vox. Sang.
26: 163- 66.
6. BIRD, G.W.G. & J. WINGHAM. 1976 More Salvia agglutinins. Vox Sang. 30:
217-219.
7. BIRD, G.W.G. & J. WINGHAM. 1977. Yet more Salvia agglutinins. Vox. Sang.
32: 121-122.
8. BIRD, G.W.G. & J. WINGHAM. 1982. More Tn-specific lectins from seeds
of Labiatae genus: Hyptis sp. Chan, Salvia lyrata and Marrubium velutinum. Clin.
Lab. Haematol. 4: 403-404.
9. BUDANTSEV, A.L. & T.A. LOBOVA. 1997. Fruit morphology, anatomy and taxonomy
of Nepeteae (Labiatae). Edinb. J. Bot. 54(2): 183-216.
10. CANTINO, P.D. 1992a. Evidence for a polyphyletic origin of the Labiatae.
Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 79: 361-379.
11. CANTINO, P.D. 1992b. Toward a phylogenetic classification of the Labiatae.
Pp 27-38, in: R.M. Harley & T. Reynolds (eds.). Advances in Labiatae Science.
Royal Botanic Gardens. Kew.
12. FERNANDEZ-ALONSO, J.L. 2003. Estudios en Labiatae de Colombia IV. Novedades
en Salvia y sinopsis de las Secciones Angulatae y Purpureae. Caldasia 25 (2):
235-281.
13. FERNÁNDEZ-ALONSO, J.L. 2005. Estudios en Labiatae de Colombia V.
Un nuevo nombre para Scutellaria leptosiphon Epling, planta redescubierta en
la Cordillera Oriental de Colombia. Rev. Acad. Colomb. Ciencias 29 (112): 319-324.
14. FERNÁNDEZ-ALONSO, J.L. 2006. Revisión taxonómica de
Salvia Sect. Siphonantha (Labiatae). Anales Jard. Bot. Madrid 59 (2): 344-348.
15. FERNÁNDEZ-ALONSO, J.L. 2008a. Estudios en Labiatae VI - Salvia yukoyukparum,
nueva specie y primer representante de la Seccion Tomentellae en Colombia. Novon
18: 38-42.
16. FERNÁNDEZ-ALONSO, J.L. 2008b. Estudios en Labiatae VII - Hibridación
en el género Salvia en Colombia y su interés horticultural. Caldasia
30(1): 21-48.
17. FERNÁNDEZ-ALONSO, J.L., N. VEGA, J.J FILGUEIRA, & G. PÉREZ.
2003. Lectin prospecting in Colombian Labiatae. A systematic-ecological approach.
Biochem. System. Ecol. 31: 617-633.
18. FERNÁNDEZ-ALONSO, J.L. & O. RIVERA. 2006. Labiatae. pp. 385-582,
in: G. Galeano & N. García (eds.): Libro Rojo de Plantas de Colombia.
Volumen 3. Serie Libros Rojos de especies amenazadas de Colombia. Instituto
Alexander von Humboldt - Instituto de Ciencias Naturales de la Universidad Nacional
de Colombia - Ministerio de Ambiente, Vivienda y Desarrollo Territorial. Bogotá.
19. FIGUEROLA, R., G. STUBING & J.B. PERIS. 1990. El complejo taxonómico
de Salvia officinalis (Sect. Salvia), en la región mediterránea
occidental. Nomenclatura y nuevas combinaciones. Fol. Bot. Misc. 7: 81-86.
20. GRUBERT, M. 1974. Studies on the distribution of myxospermy among seeds
and fruits of Angiospermae and its ecological importance. Acta Biol. Venez.
8: 315 - 551.
21. HARLEY R.M, S. ATKINS, A.L. BUDANTSEV, P.D. CANTINO, B.J. CONN, R. GRAYER,
M.M. HARLEY, R. DE KOK, J. KRESTOSKAJA, R. MORALES, A.J. PATON, O. RYDING &
T. UPSON. 2004. Labiatae, pp. 167-275, in: J.W. Kaldereit (ed.). Flowering Plants.
Dicotyledons Lamiales (except Acanthaceae including Avicenniaceae). The Families
and genera of Vascular Plants VII. Springer Verlag, Berlin.
22. HEDGE, I.C. 1970. Observations on the mucilage of Salvia fruits. Not. Royal.
Bot. Gard. Edinburgh. 30: 79-95.
23. HIROHASHI, S. H. CLAUSEN, T. YAMADA, T. Y. SHIMOSATO & S-I. H. HAKOMORI.
1985. Blood group A cross-reacting epitope defined by monoclonal antibodies
NCC Lu-35 and 81 expressed in cancer of blood group O or B individuals. Its
identification as Tn antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82: 7039-7043.
24. HOLMGREN, P.K., N.H. HOLMGREN, & L.C. BARNETT. (eds.) 1990. Index Herbariorum,
I. New York Botanical Garden. New York.
25. IWARSSON, M. & Y. HARVEY. 2003. Monograph of the genus Leonotis (Pers.)
R. Br. (Lamiaceae). Kew Bull. 58: 597-465
26. LOPEZ-PALACIOS, S. 1977. Flora de Venezuela - Verbenaceae. Universidad de
los Andes. Mérida.
27. LOPEZ-PALACIOS, S. 1986. Lista preliminar de las Verbenaceae existentes
en Colombia con algunos de sus usos y nombres vulgares. Caldasia 15: 155-176.
28. MARTÍN MOSQUERO, M.A., R. JUAN & J. PASTOR. 2004. Observaciones
micromorfológicas y anatómicas en nuculas de Prunella L. y Cleonia
L. (Lamiaceae) del suroeste de España. Acta Bot. Malacitana 29: 203-214.
29. MARTÍN MOSQUERO, M.A., R. JUAN & J. PASTOR. 2005. Observaciones
morfológicas y anatómicas en nuculas de Ballota (Lamiaceae) en
el suroeste de España. Lazaroa 26: 35-40.
30. MOORE, B.P.L. & S. MARSH. 1975. Identification of strong Sd(a+) and
Sda(a++) red cells by hemagglutinins from Salvia horminum. Transfusion 15: 132-134.
31. ORAN S.A. 1997. Nutlet anatomy of the genus Salvia in Jordan. Flora Medit.
7: 27-40.
32. PÉREZ, G. 1984. Isolation and characterization of a lectin from the
seeds of Erythrina edulis. Phytochemistry 23 : 1229-1232.
33. PÉREZ, G., N. VEGA & J.L. FERNÁNDEZ-ALONSO. 2006. Lectin
prospecting in Colombian Labiatae. A systematic-ecological approach - II. Caldasia
28: 179-196.
34. PÉREZ, G. & N. VEGA. 2007. Lamiaceae lectins. Functional Pl.
Sci. Biotechnol. 1: 288-299.
35. REALES, A., D. RIVERA, J.A. PALAZÓN & C. OBÓN. 2004. Numerical
taxonomy study of Salvia sect. Salvia (Labiatae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 145: 353-371.
36. RYDING, O 1992a. The distribution and evolution of myxocarpy in Lamiaceae.
Pp. 85-96 in: R.M. Harley, T. Reynolds (eds.), Advances in Labiatae Science.
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
37. RYDING, O. 1992b. Pericarp structure and phylogeny within Lamiaceae subfamily
Nepetoideae tribe Ocimeae. Nord. J. Bot. 12: 273-298.
38. RYDING, O. 2001. Myxocarpy in the Nepetoideae (Lamiaceae) with notes on
myxodiaspory in general. Syst. Geogr. Pl. 71: 503-514.
39. RUEDA, R.M. 1992. A new species of Aegiphila (Verbenaceae) from Colombia.
Novon 2: 167-168.
40. SUDDEE, S., A.J. PATON & J.A.N. PARNELL. 2004. A taxonomic revision
of the tribe Ocimeae in continental South East Asia. I. Introduction, Hyptidinae
/ Hanceolinae. Kew Bull. 59: 337-378.
41. UPSON, T.M. 1997. Systematics of the genus Lavandula (Lamiaceae). Ph. D.
Thesis. Reading University.
42. VEGA, N. & G. PÉREZ. 2006. Isolation and Characterisation of
a Salvia bogotensis seed lectin specific for the Tn antigen. Phytochemistry
67: 347-355.
43. WAGSTAFF, S.J., L. HICKERSON, R. SPANGLER, P.A. REEVES & R.G. OLMSTEAD.
1998. Phylogeny in Labiatae s.l., inferred from cpDNA sequences. Pl. Syst. Evol.
209: 265-274.