Publicado
Profile of the Use of Microorganisms within Environmental Management: Systematic Review 2012-2017
Perfil de usos de los microorganismos en gestión ambiental: revisión sistemática 2012-2017
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15446/ga.v23n1.83464Palabras clave:
Environmental management, microbiology, economic sectors, natural resources, sustainability (en)Gestión ambiental, microbiología, sectores económicos, recursos naturales, sostenibilidad (es)
Descargas
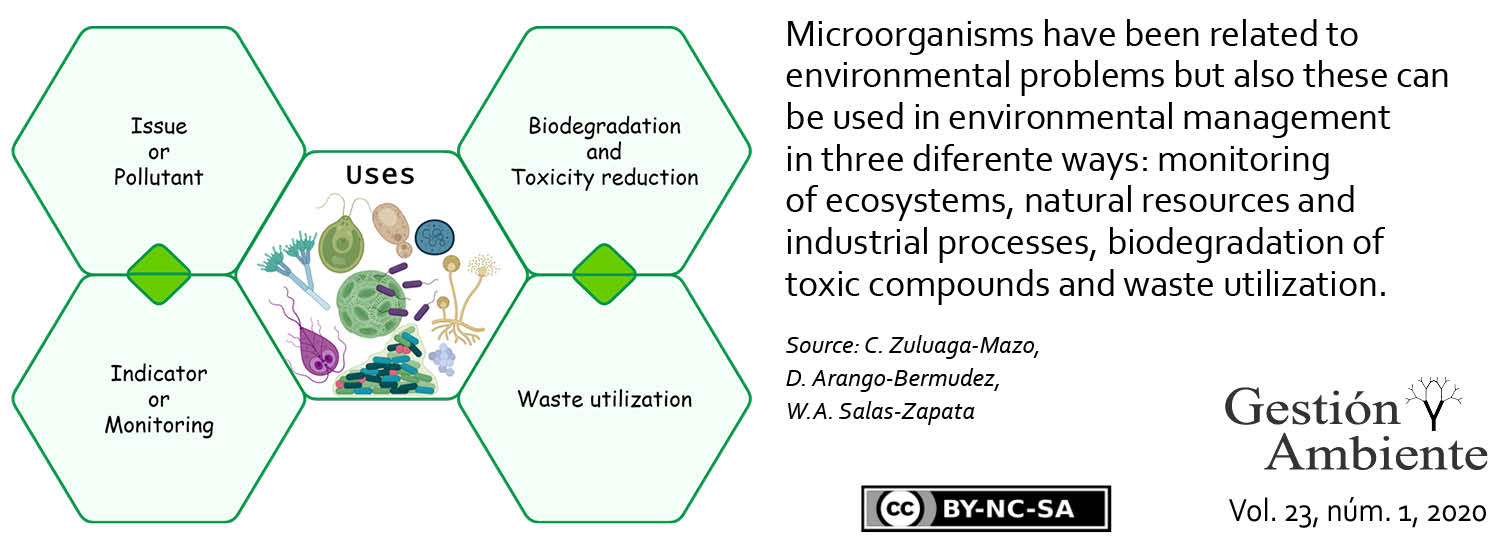
The use of microorganisms as part of environmental management action, aimed at dealing with environmental issues, results in an interesting and more environmentally friendly alternative to the conventional physicochemical decontamination methods. In this sense, a profile of the use of microorganisms in environmental management would prove helpful for people and organizations to make their processes more sustainable. However, the publications that describe the use of microorganisms within environmental management tend to show their author’s point of view, rather than the results of a systematic study in this field of knowledge. Consequently, descriptions of microorganisms, environmental issues and economic sectors involved do not necessarily reflect how developed research in microbiology and environmental management is. Therefore, the aim of this study was to describe the use given to microorganisms within environmental management, providing a profile related to the environmental issues tackled, natural resources affected, and economic sectors involved. A systematic review of scientific literature published between 2012 and 2017 led us to the description of three types of use given to microorganisms, six types of natural resources protected through such uses, ten types of environmental issues, and eight economic sectors in which the uses mentioned are applicable.
El uso de los microorganismos en acciones de gestión ambiental, con el propósito de resolver problemas ambientales, ha sido una alternativa interesante con respecto a los métodos fisicoquímicos convencionales de descontaminación porque suelen ser más amigables con el ambiente. En ese sentido, disponer de un perfil de usos de microorganismos en gestión ambiental sería de utilidad para quienes tienen responsabilidades de gestión ambiental en sus organizaciones o para quienes deben hacer más sostenibles los procesos en los que participan. No obstante, las publicaciones que caracterizan los usos de microorganismos en gestión ambiental suelen presentar la postura del autor y no el resultado de una lectura sistemática de un área de conocimiento, de tal modo que lo que se ha descrito sobre los usos de microorganismos, problemas ambientales y sectores económicos en los que dichos usos tienen aplicabilidad, no necesariamente reflejan el grado de desarrollo de los estudios en microbiología y gestión ambiental. Por esa razón, el objetivo de este estudio fue describir el perfil de usos de microorganismos en la gestión ambiental según los problemas ambientales, recursos naturales afectados y sectores económicos involucrados. Se llevó a cabo una revisión sistemática de literatura científica publicada entre el 2012 y 2017 y se encontraron tres tipos de usos de microorganismos, seis tipos de recursos naturales que son objeto de protección de esos usos, diez tipos de problemas ambientales, y ocho sectores económicos en los que tienen aplicabilidad estos usos.
Referencias
Abdel-Raouf, N., Al-Homaidan, A., Ibraheem, I., 2012. Microalgae and wastewater treatment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 19(3), 257-275. DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2012.04.005
Anand, S., 2013. Global environmental issues. Sci. Rep. 2(632), 1-9.
Bradshaw, C., Giam, X., Sodhi, N., 2010. Evaluating the relative environmental impact of countries. PLoS ONE 5(5), e10440. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010440
Cardona-Arias, J., Higuita-Gutierrez, L., Ríos-Osorio, L., 2016. Revisiones sistemáticas de la literatura científica. Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia, Medellin, Colombia.
Deshmukh, R., Khardenavis, A., Purohit, H., 2016. Diverse metabolic capacities of fungi for bioremediation. Indian J. Microbiol. 56(3), 247-264. DOI: 10.1007/s12088-016-0584-6
Elsevier Research Intelligence, 2013. Sustainability Science in a Global Landscape. Available from: https://www.elsevier.com/__data/assets/pdf_file/0018/119061/SustainabilityScienceReport-Web.pdf; consulted: May, 2019.
International Energy Agency, 2013. 2012 Annual Report. Taupo, New Zealand.
Kajikawa, Y., Tacoa, F., Yamaguchi, K., 2014. Sustainability science: the changing landscape of sustainability research. Sustain. Sci. 9(4), 431-438. DOI: 10.1007/s11625-014-0244-x
Karigar, C., Rao, S., 2011. Role of microbial enzymes in the bioremediation of pollutants: A review. Enzyme Res. 2011, 805187. DOI: 10.4061/2011/805187
Kuhad, R., 2012. Microbes and their role in sustainable development. Indian J. Microbiol. 52(2), 309-313. DOI: 10.1007/s12088-012-0267-x
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D., The PRISMA Groupf, 2010. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 8(5), 336-341. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
Mosttafiz, S., Rahman, M., Rahman, M., 2012. Biotechnology: Role of microbes in sustainable agriculture and environmental health. Internet J. Microbiol. 10(1), 1-6.
Olawumi, T., Chan, D., 2018. A scientometric review of global research on sustainability and sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 183, 231-250. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.162
Rodríguez-Becerra, M., Espinoza, G., 2002. Instrumentos de gestión ambiental. In: Rodríguez-Becerra, G., Wilk. D. (Eds.), Gestión ambiental en América Latina y El Caribe: Evolución, tendencias y principales prácticas. The World Bank, Washington, DC. pp. 175-227.
Rodriguez, D., Van den Berg, C., McMahon, A., 2012. Water papers: Investing in water infrastructure: Capital, operations and maintenance. The World Bank, Washington, DC.
Satyanarayana, T., Prakash, A., Johri, B. (Eds.), 2012. Microorganisms in environmental management: Microbes and environment. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2229-3
Steffan, S., Chikaraishi, Y., Currie, C., Horn, H., Gaines-Day, H., Pauli, J., Zapata, J., Ohkouchi, N., 2015. Microbes are trophic analogs of animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112(49), 15119-15124. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1508782112
U S Agency for International Development (USAID), 2017. U.S. Government: Global Water Strategy 2017. Washington, DC.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), 2016. Summary of the sixth global environment outlook regional assessments: Key findings and policy messages. UNEP/EA.2/INF/17. Available from: http://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/7644?show=full; consulted: February, 2019.
World Resources Institute, 2015. Measuring, mapping, and strengthening rights: the environmental democracy index. Washington, DC.
WorldoMeter, 2018. Population by Country. Database, available from: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/; consulted: november, 2018.
Cómo citar
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Descargar cita
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2020 Gestión y Ambiente

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
Los artículos que sean publicados en la revista Gestión y Ambiente, también serán publicados en el sitio web http://www.revistas.unal.edu.co/index.php/gestion/index y en formatos electrónicos como PDF, HTML, XML, entre otros. Además, en diferentes redes sociales de difusión del conocimiento. Gestión y Ambiente adopta directrices de ética por Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) sobre buenas prácticas de conducta (evitar conductas como plagio, falsificación, autoría ficticia, entre otros), describe conflictos de interés o en competencia, contribuciones de autoría y fuentes de financiación. Todo lo publicado se considerará propiedad de la revista Gestión y Ambiente, pero pueden usarse bajo la licencia Creative Commons “Reconocimiento-No Comercial-Compartir Igual International (BY-NC-SA) 4.0”















