Publicado
Preliminary Model of Potential Areas for Restoration for the Inter-Andean Valley of Cauca River (Colombia, South America) Based on Habitat Suitability Models
Modelo preliminar de áreas potenciales de restauración para el valle interandino del río Cauca (Colombia, Suramérica) basado en modelos de idoneidad de hábitat
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v29n2.103070Palabras clave:
Deciduous forest, ecological niche, landscape management, modeling, sustainable development (en)Bosque deciduo, desarrollo sostenible, gestión del paisaje, nicho ecológico, modelación (es)
Descargas
Archivos adicionales
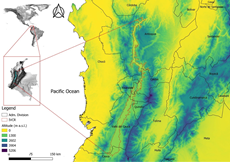
Tropical dry forests (TDF) are highly susceptible to land degradation. The inter-Andean Valley of the Cauca River (IVCR) has the most fragmented Colombian dry forests, and their restoration is essential. Here, potential areas for restoration were identified using a habitat suitability modeling (HSM) approach. TDF vascular plants and bioclimatic predictors were used. Species were selected based on threatened status, endemism, and priority level for conservation. Two sets of predictors were chosen using Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Then, with a maximum entropy algorithm, PCA and VIF models were projected for the selected species. These models were evaluated via true skill statistics (TSS) and area under the curve (AUC) statistical metrics. Models with good performance (TSS, AUC, standard deviation, variance) were ensembled, and a preliminary model where areas with suitable bioclimatic conditions for the selected species were generated. Results show that nearly 45 % of the IVCR has suitable conditions for the selected species. Although potential conflicts may arise in areas under permanent or semipermanent crops which represent more than 80 % of the IVCR, cropland mosaics, and natural and seminatural land covers might provide alternative solutions to reduce the land-use conflict. The potential areas for restoration identified in this study may provide a comprehensive framework for environmental impact and regional risk assessments related to the current land use and land cover change dynamics. Also, they may provide relevant information for designing landscape restoration programs as an adaptive strategy toward climate change.
Los bosques secos tropicales (BsT) son ecosistemas vulnerables a la degradación. En el Valle Interandino del Río Cauca (VIRC), los BsT están muy fragmentados y necesitan restauración. Para identificar áreas potenciales de restauración se aplicó modelación de idoneidad del hábitat (HSM) utilizando plantas vasculares del BsT y predictores bioclimáticos. Se escogieron especies según su amenaza, endemismo y prioridad de conservación, y las variables según el factor de inflación de varianza (FIV) y el análisis de componentes principales (ACP). Usando un algoritmo de máxima entropía y predictores ACP y FIV seleccionados, se identificaron áreas bioclimáticas idóneas para las especies seleccionadas. Estos modelos se evaluaron a través de las métricas True skill statistic (TSS) y del área bajo la curva (AUC). Modelos con buen desempeño (TSS, AUC, desviación estándar, varianza) se ensamblaron en un modelo preliminar donde se observó que cerca del 45 % del VIRC tiene condiciones adecuadas. Aunque pueden darse conflictos potenciales para la restauración en áreas con cultivos permanentes o semipermanentes (80 % del VIRC), los mosaicos de tierras de cultivo y las coberturas naturales y seminaturales ofrecen soluciones alternativas para reducirlos. Las áreas potenciales para la restauración identificadas en este estudio pueden proporcionar un marco integral para estudios del impacto ambiental y de riesgo regional relacionadas con el uso actual de la tierra y las dinámicas de cambios de uso. Asimismo, esta investigación aporta elementos importantes para el diseño de programas de restauración del paisaje como estrategia de adaptación al cambio climático.
Referencias
Allouche, O., Tsoar, A. and Kadmon, R. (2006). Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). Journal of Applied Ecology, 43(6), 1223–1232. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2006.01214.x
Alvarado-Solano, D. P. and Otero Ospina, J. T. (2017). Áreas naturales de bosque seco tropical en el Valle del Cauca, Colombia: una oportunidad para la restauración. Biota Colombiana, 18, 9–34. https://doi.org/10.21068/c2017v18s01a01
Alvarado-Solano, D. P. and Otero Ospina, J. T. (2015). Distribución espacial del bosque seco tropical en el Valle del Cauca, Colombia. Acta Biológica Colombiana, 20(3), 141-153. https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v20n2.46703
Araujo Bortoleto, L., Montagnani Figueira, C. J., Dunning, J. B., Rodgers, J., and Da Silva, A. M. (2016). Suitability index for restoration in landscapes: An alternative proposal for restoration projects. Ecological Indicators, 60, 724–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.08.002
Arcila Cardona, A. M., Valderrama Ardila, C. and Chacón de Ulloa, P. (2012). Estado de fragmentación del bosque seco de la cuenca alta del río Cauca, Colombia. Biota Colombiana, 13, 86–101.
Barbosa, A. M. (2015). FuzzySim: Applying fuzzy logic to binary similarity indices in ecology. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6(7), 853–858. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12372
Boria, R. A. and Blois, J. L. (2018). The effect of large sample sizes on ecological niche models: Analysis using a North American rodent, Peromyscus maniculatus. Ecological Modelling, 386, 83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2018.08.013
Chazdon, R. L., Brancalion, P. H. S., Lamb, D., Laestadius, L., Calmon, M. and Kumar, C. (2017). A Policy-Driven Knowledge Agenda for Global Forest and Landscape Restoration. Conservation Letters, 10(1), 125–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/conl.12220
Corporación Autónoma Regional del Valle del Cauca. (2015). Plan de Gestión Regional Ambiental 2015 – 2036. 302 pp.
Dantas, B. F., Moura, M. S. B., Pelacani, C. R., Angelotti, F., Taura, T. A., Oliveira, G. M., Bispo, J. S., Matias, J. R., Silva, F. F. S., Pritchard, H. W. and Seal, C. E. (2020). Rainfall, not soil temperature, will limit the seed germination of dry forest species with climate change. Oecologia, 192(2), 529–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-019-04575-x
Elith, J., Phillips, S. J., Hastie, T., Dudík, M., Chee, Y. E. and Yates, C. J. (2011). A statistical explanation of MaxEnt for ecologists. Diversity and Distributions, 17(1), 43–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2010.00725.x
Fajardo, L., Rodríguez, J. P., González, V. and Briceño-Linares, J. M. (2013). Restoration of a degraded tropical dry forest in Macanao, Venezuela. Journal of Arid Environments, 88, 236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2012.08.009
Ferrer-Paris, J. R., Zager, I., Keith, D. A., Oliveira-Miranda, M. A., Rodríguez, J. P., Josse, C., González-Gil, M., Miller, R. M., Zambrana-Torrelio, C. and Barrow, E. (2019). An ecosystem risk assessment of temperate and tropical forests of the Americas with an outlook on future conservation strategies. Conservation Letters, 12(2), e12623. https://doi.org/10.1111/conl.12623
Fois, M., Cuena-Lombraña, A., Fenu, G., Cogoni, D. and Bacchetta, G. (2018). Does a correlation exist between environmental suitability models and plant population parameters? An experimental approach to measure the influence of disturbances and environmental changes. Ecological Indicators, 86, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.12.009
Fourcade, Y., Engler, J. O., Rödder, D. and Secondi, J. (2014). Mapping species distributions with MAXENT using a geographically biased sample of presence data: A performance assessment of methods for correcting sampling bias. PLOS One, 9, e97122. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097122
Franklin, J., Andrade, R., Daniels, M. L., Fairbairn, P., Fandino, M. C., Gillespie, T. W., González, G., Gonzalez, O., Imbert, D., Kapos, V., Kelly, D. L., Marcano-Vega, H., Meléndez-Ackerman, E. J., McLaren, K. P., McDonald, M. A., Ripplinger, J., Rojas-Sandoval, J., Ross, M. S., Ruiz, J., Steadman, D. W., Tanner, E. V. J., Terrill, I. and Vennetier, M. (2018). Geographical ecology of dry forest tree communities in the West Indies. Journal of Biogeography, 45(5), 1168–1181. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.13198
García-Callejas, D. and Araújo, M. B. (2016). The effects of model and data complexity on predictions from species distribution models. Ecological Modelling, 326, 4–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2015.06.002
García, H., Corzo, G., Isaacs, P. and Etter, A. (2014). Distribución y estado actual de los remanentes del bioma de bosque seco tropical en Colombia: Insumos para su gestión. In: Pizano, C. and H. García (Eds.), El Bosque Seco Tropical En Colombia. Instituto de Investigación en Recursos Biológicos Alexander von Humboldt (pp. 228–251). http://repository.humboldt.org.co/handle/20.500.11761/9333
Hao, T., Elith, J., Guillera-Arroita, G. and Lahoz-Monfort, J. J. (2019). A review of evidence about use and performance of species distribution modelling ensembles like BIOMOD. Diversity and Distributions, 25(5), 839-852. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12892
Holdridge, L. R. (1967). Life zone ecology. Tropical Science Center, San José. http://reddcr.go.cr/sites/default/files/centro-de-documentacion/holdridge_1966_-_life_zone_ecology.pdf
Hua, Y., Cui, B., He, W. and Cai, Y., (2016). Identifying potential restoration areas of freshwater wetlands in a river delta. Ecological Indicators, 71, 438–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.07.036
Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales, Instituto de Investigación de Recursos Biológicos Alexander von Humboldt, Instituto de Investigaciones Marinas y Costeras José Benito Vives de Andréis, e Instituto Geográfico Agustín Codazzi (2017). Mapa de ecosistemas continentales, costeros y marinos de Colombia (MEC), escala 1:100.000.
Jarnevich, C. S., Stohlgren, T. J., Kumar, S., Morisette, J. T. and Holcombe, T. R. (2015). Caveats for correlative species distribution modeling. Ecological Informatics, 29(1), 6–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2015.06.007
Kaky, E., Nolan, V., Alatawi, A. and Gilbert, F. (2020). A comparison between Ensemble and MaxEnt species distribution modelling approaches for conservation: A case study with Egyptian medicinal plants. Ecological Informatics, 60, 101150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2020.101150
Kramer-Schadt, S., Niedballa, J., Pilgrim, J. D., Schröder, B., Lindenborn, J., Reinfelder, V., Stillfried, M., Heckmann, I., Scharf, A. K., Augeri, D. M., Cheyne, S. M., Hearn, A. J., Ross, J., Macdonald, D. W., Mathai, J., Eaton, J., Marshall, A. J., Semiadi, G., Rustam, R., Bernardo, H., Raymond, A., Samejima,H., Duckworth, J. W., Breitenmoser-Würsten, C., Belant, J. L., Hofer, H. and Wilting, A. (2013). The importance of correcting for sampling bias in MaxEnt species distribution models. Diversity and Distributions, 19(11), 1366–1379. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12096
Liu, C., White, M. and Newell, G. (2013). Selecting thresholds for the prediction of species occurrence with presence-only data. Journal of Biogeography, 40(4), 778–789. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12058
Loreau, M., Mouquet, N. and Gonzalez, A. (2003). Biodiversity as spatial insurance in heterogeneous landscapes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(22), 12765–12770. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2235465100
Maiorano, L., Chiaverini, L., Falco, M., and Ciucci, P. (2019). Combining multi-state species distribution models, mortality estimates, and landscape connectivity to model potential species distribution for endangered species in human dominated landscapes. Biological Conservation, 237, 19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2019.06.014
Meli, P., Rey-Benayas, J. M. and Brancalion, P. H. S. (2019). Balancing land sharing and sparing approaches to promote forest and landscape restoration in agricultural landscapes: Land approaches for forest landscape restoration. Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation, 17(4), 201–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecon.2019.09.002
Mestre, F., Risk, B. B., Mira, A., Beja, P. and Pita, R. (2017). A metapopulation approach to predict species range shifts under different climate change and landscape connectivity scenarios. Ecological Modelling, 359, 406–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.06.013
Miles, L., Newton, A. C., DeFries, R. S., Ravilious, C., May, I., Blyth, S., Kapos, V. and Gordon, J. E. (2006). A global overview of the conservation status of tropical dry forests. Journal of Biogeography. 33(3), 491–505. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2005.01424.x
Miranda, E. B. P., Menezes, J. F. S., Farias, C. C. L., Munn, C., & Peres, C. A. (2019). Species distribution modeling reveals strongholds and potential reintroduction areas for the world’s largest eagle. PLoS ONE, 14(5), e0216323. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216323
NASAJPL. (2013). NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission Global 1 arc second. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC. https://doi.org/10.5067/MEaSUREs/SRTM/SRTMGL1.003
Neves, D. M., Dexter, K. G., Pennington, R. T., Bueno, M. L. and Oliveira Filho, A. T. (2015). Environmental and historical controls of floristic composition across the South American Dry Diagonal. Journal of Biogeography, 42(8), 1566–1576. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12529
Nkonya, E., Anderson, W., Kato, E., Koo, J., Mirzabaev, A., von Braun, J., and Meyer, S. (2015). Global cost of land degradation. In Economics of Land Degradation and Improvement–A Global Assessment for Sustainable Development (pp. 117–165). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19168-3_6
Pando, J. P; Ibanez, T; Franklin, J; Pau, S; Keppel, G; Rivas-Torres G, Shin, M. E. Welch, T. (2021) Global tropical dry forest extent and cover: A comparative study of bioclimatic definitions using two climatic data sets. PLoS ONE, 16(5), e0252063. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252063
Peres-Neto, P. R., Jackson, D. A., and Somers, K. M. (2003). Giving meaningful interpretation to ordination axes: Assessing loading significance in principal component analysis. Ecology, 84(9), 2347–2363. https://doi.org/10.1890/00-0634
Phillips, S. J. and Dudík, M. (2008). Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: new extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography, 31(2), 161–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0906-7590.2008.5203.x
Poirazidis, K., Bontzorlos, V., Xofis, P., Zakkak, S., Xirouchakis, S., Grigoriadou, E., Kechagioglou, S., Gasteratos, I., Alivizatos, H., & Panagiotopoulou, M. (2019). Bioclimatic and environmental suitability models for capercaillie (Tetrao urogallus) conservation: Identification of optimal and marginal areas in Rodopi Mountain-Range National Park (Northern Greece). Global Ecology and Conservation, 17, e00526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00526
Radosavljevic, A. and Anderson, R. P. (2014.) Making better Maxent models of species distributions: complexity, overfitting and evaluation. Journal of Biogeography, 41(4), 629–643. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12227
Reed, J., Van Vianen, J., Deakin, E. L., Barlow, J. and Sunderland, T. (2016). Integrated landscape approaches to managing social and environmental issues in the tropics: learning from the past to guide the future. Global Change Biology, 22(7), 2540–2554. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13284
RStudio Team (2021). RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, PBC, Boston, MA URL http://www.rstudio.com/.
Salas, E. A. L., Seamster, V. A., Harings, N. M., Boykin, K. G., Alvarez, G. and Dixon, K. W. (2017). Projected future bioclimate-envelope suitability for reptile and amphibian species of concern in South Central USA. Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 12, 522–547.
Santana Rodriguez, L. M. y Vásquez Sanchez, J. (2002). Características geográficas del Departamento del Valle del Cauca. Entorno Geográfico, 1. https://doi.org/10.25100/eg.v0i1.3556
Schild, J. E. M., Vermaat, J. E. and van Bodegom, P. M. (2018). Differential effects of valuation method and ecosystem type on the monetary valuation of dryland ecosystem services: A quantitative analysis. Journal of Arid Environments, 159, 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2017.09.001
Siyum, Z. G. (2020). Tropical dry forest dynamics in the context of climate change: syntheses of drivers, gaps, and management perspectives. Ecological Processes, 9 (1), 25. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-020-00229-6
Somodi, I., Lepesi, N. and Botta-Dukát, Z. (2017). Prevalence dependence in model goodness measures with special emphasis on true skill statistics. Ecology and Evolution, 7(3), 863–872. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.2654
Thuiller, W., Guéguen, M., Renaud, J., Karger, D. N., & Zimmermann, N. E. (2019). Uncertainty in ensembles of global biodiversity scenarios. Nature Communications, 10(1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09519-w
Török, P.and Helm, A. (2017). Ecological theory provides strong support for habitat restoration. Biological Conservation, 206, 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2016.12.024
van der Plas, F., Allan, E., Fischer, M., Alt, F., Arndt, H., Binkenstein, J., Blaser, S., Blüthgen, N., Böhm, S., Hölzel, N., Klaus, V.H., Kleinebecker, T., Morris, K., Oelmann, Y., Prati, D., Renner, S.C., Rillig, M.C., Schaefer, H.M., Schloter, M., Schmitt, B., Schöning, I., Schrumpf, M., Solly, E. F., Sorkau, E., Steckel, J., Steffan-Dewenter, I., Stempfhuber, B., Tschapka, M., Weiner, C., Weisser, W., Werner, M., Westphal, C., Wilcke, W. andManning, P. (2019). Towards the development of general rules describing landscape heterogeneity-multifunctionality relationships. Journal of Applied Ecology, 56, 168–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13260
Vargas, W. (2012). Los bosques secos del Valle del Cauca, Colombia: una aproximación a su flora actual. Biota Colombiana, 13, 102–164. http://revistas.humboldt.org.co/index.php/biota/article/view/265
Zellmer, A. J., Claisse, J. T., Williams, C. M., Schwab, S., & Pondella, D. J. (2019). Predicting Optimal Sites for Ecosystem Restoration Using Stacked-Species Distribution Modeling. Frontiers in Marine Science, 6, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00003
Zhong, Y., Xue, Z., Jiang, M., Liu, B., & Wang, G. (2021). The application of species distribution modeling in wetland restoration: A case study in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Ecological Indicators, 121, 107137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107137
Cómo citar
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Descargar cita
CrossRef Cited-by
1. Yoseth David Blanquiceth Tamara, Sebastián Cuadrado-Rios, Juan Pretelt, Juan Urzola, María Ozuna Ortega, Julio Chacón-Pacheco, Hugo Mantilla-Meluk. (2025). First records and extension of the geographic distribution of Cynomops kuizha (Chiroptera: Molossidae) in the Colombian Caribbean. Mammalia, 89(1), p.103. https://doi.org/10.1515/mammalia-2024-0097.
2. Boyi Cui, Yuanxiang Wu, Mengmeng Li. (2025). Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Building Materials and Construction. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering. 664, p.193. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-7687-3_18.
Dimensions
PlumX
Visitas a la página del resumen del artículo
Descargas
Licencia

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
1. La aceptación de manuscritos por parte de la revista implicará, además de su edición electrónica de acceso abierto bajo licencia Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 (CC BY NC SA), la inclusión y difusión del texto completo a través del repositorio institucional de la Universidad Nacional de Colombia y en todas aquellas bases de datos especializadas que el editor considere adecuadas para su indización con miras a incrementar la visibilidad de la revista.
2. Acta Biológica Colombiana permite a los autores archivar, descargar y compartir, la versión final publicada, así como las versiones pre-print y post-print incluyendo un encabezado con la referencia bibliográfica del articulo publicado.
3. Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
4. Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos institucionales, en su página web o en redes sociales cientificas como Academia, Researchgate; Mendelay) lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).