Publicado
Modeling the impact of supplementary cementitious materials on compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete forest-random approach
Modelación del impacto de los materiales cementantes suplementarios en la resistencia a compresión de los concretos con agregados reciclados - enfoque por bosques aleatorios
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v91n231.107967Palabras clave:
Random Forest algorithm; compressive strength; supplementary cementitious materials; recycled concrete aggregate; reactivity modulus; silica modulus; alumina modulus; sustainability (en)Algoritmo de bosques aleatorios; resistencia a la compresión; materiales cementantes suplementarios; agregados de concreto reciclado; módulo de reactividad; módulo de sílice; módulo de alúmina; sostenibilidad (es)
Descargas
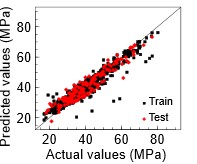
Recycled concrete aggregates (RCAs) and supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) may substitute some cement and natural aggregates (NA) in concrete manufacturing. However, their effects on recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) compressive strength are difficult to model. Reactivity, silica, and alumina modulus were examined for cementitious materials' chemical complexity. Random Forest approaches were developed to predict and analyze RAC compressive strength. Even with RCAs and SCMs, the RF model accurately estimated concrete compressive strength. The Variable Importance (VI) research examined how input factors affected RAC compressive strength. VI indicated that silica fume contributes most to RAC compressive strength, followed by cementitious materials' reactivity modulus, cement content, silica modulus, fine natural aggregate content, and coarse natural aggregate dosage. The water dosage, water/binder ratio, and RCA content lower the RAC compressive strength. As a result, to highlight, the amount of SCM was not significant, but its nature was (i.e., hydraulic, silica pozzolanic, or alumina pozzolanic).
Los agregados de concreto reciclado (ACR) y los materiales cementantes suplementarios (MCS) pueden sustituir parcialmente cemento y agregados naturales (NA) en la fabricación de concreto. Sin embargo, sus efectos sobre la resistencia a la compresión del concreto con agregados reciclados (CAR) son difíciles de modelar. Se examinaron los módulos de reactividad, sílice y alúmina para determinar la complejidad química de los materiales cementosos. Se desarrollaron enfoques de Random Forest para predecir y analizar la resistencia a la compresión de los CAR. Incluso con ACR y MCS, el modelo de RF estimó con precisión la resistencia a la compresión del concreto. El análisis de importancia de variable (IV) examinó cómo los factores de entrada afectaron a la resistencia a la compresión del RAC. IV indicó que el humo de sílice contribuye más a la resistencia a la compresión del CAR, seguido del módulo de reactividad de los materiales cementantes, el contenido de cemento, el módulo de sílice, el contenido de agregados naturales finos y la dosificación de agregados naturales gruesos. La dosificación de agua, la relación agua/cemento y el contenido de ACR reducen la resistencia a la compresión de CAR. Como resultado a destacar, la cantidad de MCS no fue significativa, pero sí su naturaleza (es decir, hidráulica, sílice puzolánica o alúmina puzolánica).
Referencias
Walberg, D., Solid and timber construction in residential buildings/Massiv‐und Holzbau bei Wohngebäuden, Mauerwerk, 20(1), pp.16-31, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/dama.201600685. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/dama.201600685
Deutscher, N., Global Cement Production from 1990 to 2030 (in million metric tons), [online]. 2019. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/373845/global-cement-production-forecast/.
Group, F., Global Demand for Construction Aggregates to Exceed 48 Billion Metric Tons in 2015, Concrete Construction, 2012.
Wang, B., Yan, L., Fu, Q., and Kasal, B., A comprehensive review on recycled aggregate and recycled aggregate concrete, Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 171, art. 105565, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105565 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105565
Nixon, P., Recycled concrete as an aggregate for concrete—a review, Matériaux et Construction 11, pp. 371-378, 1978. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02473878 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02473878
Slattery, K., Global developments in the aggregate industry, Global Aggregates Information, Network, 2014.
Zhang, Y., Qin, H., Sun, W., Hao, D., and Ning, Z., Preliminary study on the proportion design of recycled aggregate concrete, China. Concrete and Cement Products 1, pp 7-9, 2002.
Poon, C.S., Shui, Z., and Lam, L., Effect of microstructure of ITZ on compressive strength of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates, Construction and Building Materials 18(6), pp. 461-468, 2004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2004.03.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2004.03.005
Tam, V.W., Gao, X., and Tam, C.M., Microstructural analysis of recycled aggregate concrete produced from two-stage mixing approach, Cement and concrete research 35(6), pp. 1195-1203, 2005. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.10.025 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.10.025
Etxeberria, M., Vázquez, E., and Mari, A., Microstructure analysis of hardened recycled aggregate concrete, Mag. Concr. Res. 58(10), pp. 683-690, 2006.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/macr.2006.58.10.683. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/macr.2006.58.10.683
Xiao, J., Experimental investigation on complete stress-strain curve of recycled concrete under uniaxial loading, Journal-Tongji University 35(11), art. 1445, 2007.
Hu, Q., Song, C., and Zou, C., Experimental research on the mechanical properties of recycled concrete, Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 41(4), pp. 33-36, 2009.
Zhou, J., He, H., Meng, X., and Yang, Y., Basic mechanical properties of recycled concrete experimental study, Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University(Natural Science). 26(3), pp. 464-468, 2010.
Li, J., Xiao, J., and Huang, J., Influence of recycled coarse aggregate replacement percentages on compressive strength of concrete, Jianzhu Cailiao Xuebao/Journal of Building Materials, 9(3), pp. 297-301, 2006
Tang, J., Preliminary study on compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete, Sichuan Building Science. 33(4), pp. 183-186, 2007.
Jin, C., Wang, X., Akinkurolere, O., and Jiang, C., Experimental research on the conversion relationships between the mechanical performance indexes of recycled concrete, Chinese Concrete Journal 11, pp. 37-39, 2008.
Kou, S.C., Poon, C.S., and Chan, D., Influence of fly ash as cement replacement on the properties of recycled aggregate concrete, J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 19(9), pp. 709-717, 2007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2007)19:9(709). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2007)19:9(709)
Xiao, J.-Z., and Lan, Y., Investigation on the tensile behavior of recycled aggregate concrete, Jianzhu Cailiao Xuebao. Journal of Building Materials, 9(2), pp. 154-158, 2006.
Al-Bayati, H.K.A., Das, P.K., Tighe, S.L., and Baaj, H., Evaluation of various treatment methods for enhancing the physical and morphological properties of coarse recycled concrete aggregate, Construction and Building Materials, 112, pp. 284-298, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.176
Makul, N., Fediuk, R., Amran, M., Zeyad, A.M., Klyuev, S., Chulkova, I., Ozbakkaloglu, T., Vatin, N., Karelina, M., and Azevedo, A., Design strategy for recycled aggregate concrete: a review of status and future perspectives, Crystals 11(6), art. 695, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060695. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060695
Liu, Q., Xiao, J., and Sun, Z., Experimental study on the failure mechanism of recycled concrete, Cement and Concrete Research, 41(10), pp. 1050-1057, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.06.007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.06.007
Buck, A.D., Recycled concrete as a source of aggregate: final report, United States. Army. Corps of Engineers, Concrete Technology Information Analysis Center, U.S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, Concrete Laboratory (U.S.), Waterways Experiment Station, ed., USA, 1976, 34 P.
Hu, B., Liu, B.-k., and Zhang, L., Chloride ion permeability test and analysis for recycled concrete, Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 32, pp. 1240-1243, 2009.
Zhang, J., Li, Q., Du, J., and Li, X., Experimental study on mineral admixture and recycled aggregates affecting the rapid chloride permeability of high-performance recycled concrete, Chin. Concr. 2, pp. 94-97, 2009.
Du, T., Li, H., Guo, T., and Zhou, Z., Test study on the resistance of chloride ion penetration of recycled aggregate concrete, Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 28(5), pp. 33-36, 2006.
Lei, Z., and Jin, W., The study on early drying shrinkage of recycled aggregate concrete, in: 2nd International Conference on Waste Engineering and Management-ICWEM 2010, RILEM Publications SARL, 2010, pp. 568-575.
Zhang, J., Du, H., Zhang, C., and Li, Q., Influence of mineral admixture and recycled aggregate on shrinkage of concrete, Journal of Qingdao Technological University, 34(4), pp. 145-149, 2009.
Zhou, J., and Jiang, H., Experimental study on shear behavior of recycled coarse aggregate concrete beams, Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University, 25(4), pp. 683-688, 2009.
Wang, H., Sun, X., Wang, J., and Monteiro, P.J., Permeability of concrete with recycled concrete aggregate and pozzolanic materials under stress, Materials 9(4), art. 252, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040252. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040252
Kurad, R., Silvestre, J.D., de Brito, J., and Ahmed, H., Effect of incorporation of high volume of recycled concrete aggregates and fly ash on the strength and global warming potential of concrete, Journal of Cleaner Production, 166, pp. 485-502, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.236 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.236
Almeida, A., and Cunha, J., The implementation of an Activity-Based Costing (ABC) system in a manufacturing company, Procedia manufacturing, 13, pp. 932-939, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.09.162 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.09.162
Poon, C., Azhar, S., and Kou, S., Recycled aggregates for concrete applications, in: Proceeding of the Materials Science and Technology in Engineering Conference—Now, New and Next, Hong Kong China, 2003.
Poon, C.S., Kou, S., and Lam, L., Use of recycled aggregates in molded concrete bricks and blocks, Construction and Building Materials, 16(5), pp. 281-289, 2002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-0618(02)00019-3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-0618(02)00019-3
Tam, V., Soomro, M., and Evangelista, A., A review of recycled aggregate in concrete applications (2000–2017), Construction and Building materials 172, pp. 272-292, 2018. _DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.240 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.240
Colaboradores de Wikipedia. Random forest Wikipedia, La enciclopedia libre, Ed., [en línea]. 2023. [Accessed February 19th of 2023]. Available at: https://es.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Random_forest&oldid=153545477, [online]. 2023
Fawagreh, K., Gaber, M.M., and Elyan, E., Random forests: from early developments to recent advancements, Systems Science & Control Engineering, 2(1), pp. 602-609, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/21642583.2014.956265 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/21642583.2014.956265
Breiman, L., Random forests, Machine Learning, 45, pp. 5-32, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Breiman, L, Bagging predictors, Machine Learning 24, pp. 123-140, 1996. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00058655. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00058655
Ho, T.K., Random decision forests, in: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on document analysis and recognition, IEEE, pp. 278-282, 1995.
Amit, Y., Geman, D., Shape quantization and recognition with randomized trees, Neural computation 9(7) pp. 1545-1588, 1995. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.7.1545
Pham, B.T., Qi, C., Ho, L.S., Nguyen-Thoi, T., Al-Ansari, N., Nguyen, M.D., Nguyen, H.D., Ly, H.-B., Le, H.V., and Prakash, I., A novel hybrid soft computing model using random forest and particle swarm optimization for estimation of undrained shear strength of soil, Sustainability, 12(6), art. 2218, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062218. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062218
Zhang, W., Wu, C., Zhong, H., Li, Y., and Wang, L., Prediction of undrained shear strength using extreme gradient boosting and random forest based on Bayesian optimization, Geoscience Frontiers, 12(1), pp. 469-477, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.03.007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.03.007
Tran, Q.A., Ho, L.S., Le, H.V., Prakash, I., and Pham, B.T., Estimation of the undrained shear strength of sensitive clays using optimized inference intelligence system, Neural Computing and Applications 34(10), pp. 7835-7849, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-06891-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-06891-5
Zhou, J., Li, E., Wei, H., Li, C., Qiao, Q., and Armaghani, D.J., Random forests and cubist algorithms for predicting shear strengths of rockfill materials, Applied Sciences 9(8), art. 1621, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081621. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081621
Zhou, Y., Li, S., Zhou, C., and Luo, H., Intelligent approach based on random forest for safety risk prediction of deep foundation pit in subway stations, Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering 33(1), art. 05018004, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000796 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000796
Pham, T.A., Ly, H.-B., Tran, V.Q., Giap, L.V., Vu, H.-L.T., and Duong, H.-A.T., Prediction of pile axial bearing capacity using artificial neural network and random forest, Applied Sciences 10(5), id. 1871, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051871 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051871
Zhang, W., Wu, C., Li, Y., Wang, L., and Samui, P., Assessment of pile drivability using random forest regression and multivariate adaptive regression splines, Georisk: Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards 15(1), pp. 27-40, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2019.1674340. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17499518.2019.1674340
Kang, K., and Ryu, H., Predicting types of occupational accidents at construction sites in Korea using random forest model, Safety Science 120 pp. 226-236, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.06.034. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.06.034
Yaseen, Z.M., Ali, Z.H., Salih, S.Q., and Al-Ansari, N., Prediction of risk delay in construction projects using a hybrid artificial intelligence model, Sustainability 12(4), art. 1514, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041514. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041514
Pan, Y., and Zhang, L., Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: A critical review and future trends, Automation in Construction 122, art. 103517, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103517. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103517
Daneshvar, D., and Behnood, A., Estimation of the dynamic modulus of asphalt concretes using random forests algorithm, International Journal of Pavement Engineering 23(2), pp. 250-260, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2020.1741587 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2020.1741587
Luo, X., Wang, F., Bhandari, S., Wang, N., and Qiu, X., Effectiveness evaluation and influencing factor analysis of pavement seal coat treatments using random forests, Construction and Building Materials 282, art. 122688, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122688. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122688
Ehsani, M., Moghadas Nejad, F., and Hajikarimi, P., Developing an optimized faulting prediction model in Jointed Plain Concrete Pavement using artificial neural networks and random forest methods, International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 24(2), pp. 1-16, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2022.2057975 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2022.2057975
Vakharia, V., and Gujar, R., Prediction of compressive strength and portland cement composition using cross-validation and feature ranking techniques, Construction and Building Materials 225, pp. 292-301, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.224 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.224
Zhang, J., Ma, G., Huang, Y., Aslani, F., and Nener, B., Modelling uniaxial compressive strength of lightweight self-compacting concrete using random forest regression, Construction and Building Materials 210, pp. 713-719, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.189. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.189
Han, Q., Gui, C., Xu, J., and Lacidogna, G., A generalized method to predict the compressive strength of high-performance concrete by improved random forest algorithm, Construction and Building Materials, 226, pp. 734-742, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.315. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.315
Sun, Y., Li, G., Zhang, J., and Qian, D., Prediction of the strength of rubberized concrete by an evolved random forest model, Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, pp. 1-7, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5198583. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5198583
Farooq, F., Nasir Amin, M., Khan, K., Rehan Sadiq, M., Javed, M.F., Aslam, F., and Alyousef, R., A comparative study of random forest and genetic engineering programming for the prediction of compressive strength of high strength concrete (HSC), Applied Sciences, 10(20), art. 73300, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207330 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207330
Abellán-García, J., Four-layer perceptron approach for strength prediction of UHPC, Construction and Building Materials 256, art. 119465, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119465. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119465
Huang, J., Duan, T., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, J., and Lei, Y., Predicting the permeability of pervious concrete based on the beetle antennae search algorithm and random forest model, Adv. Civ. Eng. Special Issue 2020, pp.1-11, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8863181 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8863181
Khan, M.A., Memon, S.A., Farooq, F., Javed, M.F., Aslam, F., and Alyousef, R., Compressive strength of fly-ash-based geopolymer concrete by gene expression programming and random forest, Adv. Civ. Eng. Special Issue 2021, pp. 1-17, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6618407. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6618407
Khambra, G., and Shukla, P., Novel machine learning applications on fly ash based concrete: an overview, Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021.
Abellan-Garcia, J., and Guzmán-Guzmán, J.S., Random forest-based optimization of UHPFRC under ductility requirements for seismic retrofitting applications, Construction and Building Materials, 285, art. 122869, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122869 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122869
Xie, T., and Visintin, P., A unified approach for mix design of concrete containing supplementary cementitious materials based on reactivity moduli, Journal of Cleaner Production, 203, pp. 68-82, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.254 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.254
Limbachiya, M., Marrocchino, E., and Koulouris, A., Chemical–mineralogical characterisation of coarse recycled concrete aggregate, Waste Management, 27(2), pp. 201-208, 2007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.01.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.01.005
Aggarwal, C.C., An introduction to outlier analysis, Springer, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47578-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47578-3_1
Pimentel, M.A., Clifton, D.A., Clifton, L., and Tarassenko, L., A review of novelty detection, Signal Processing, 99, pp. 215-249, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.12.026. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.12.026
Zimek, A., Schubert, E., and Kriegel, H.P., A survey on unsupervised outlier detection in high‐dimensional numerical data, Statistical Analysis and Data Mining: the ASA Data Science Journal, 5(5), pp. 363-387, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sam.11161 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sam.11161
Wikipedia contributors. Outlier. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Ed., [online]. 2023. [Accessed February 18th of 2023]. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Outlier&oldid=1181881199
Atkinson, A.C., and Riani, M., Robust diagnostic regression analysis, Springer, 2000. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1160-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1160-0
Härdle, W.K., and Simar, L., Applied multivariate statistical analysis, Springer Nature, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1160-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26006-4
Abellán-García, J., Artificial neural network model for strength prediction of ultra-high-performance concre, ACI Materials Journal 118(4), pp. 1-12, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14359/51732710 DOI: https://doi.org/10.14359/51732710
Everitt, B., and Hothorn, T., An introduction to applied multivariate analysis with R, Springer Science & Business Media, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9650-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9650-3
Breiman, L., Friedman, J., Olshen, R., and Stone, C., Classification and Regression Trees. Chapman and Hall, Eds., New York, USA, 1984.
Genuer R., and Poggi J-M., Random Forests with R.; 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56485-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56485-8
Dietterich, T.G., Ensemble methods in machine learning. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Vol 1857 LNCS., pp. 1-15, 2000. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45014-9_1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45014-9_1
Auret, L., and Aldrich, C., Interpretation of nonlinear relationships between process variables by use of random forests. Miner Eng. 35, pp. 27-42, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2012.05.008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2012.05.008
Oshiro, T.M., Perez, P.S., and Baranauskas, J.A., How many trees in a random forest? Lect Notes Comput Sci (including SubserLect Notes ArtifIntellLect Notes Bioinformatics), LNAI(May), pp. 154-168, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31537-4_13 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31537-4_13
Naser, M.Z., and Alavi, A.H., Error metrics and performance fitness indicators for artificial intelligence and machine learning in engineering and sciences. Archit Struct Constr., 3, pp. 499-517, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44150-021-00015-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44150-021-00015-8
R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Computing RF for S, eds., Vienna, Austria, 2018.
Çakır, Ö., and Sofyanlı, Ö., Influence of silica fume on mechanical and physical properties of recycled aggregate concrete, HBRC J, 11(2), pp. 157-166, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbrcj.2014.06.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbrcj.2014.06.002
Dhandapani, Y., and Santhanam, M., Investigation on the microstructure-related characteristics to elucidate performance of composite cement with limestone-calcined clay combination. CemConcr Res., 129 (December 2019), art. 105959, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2019.105959 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2019.105959
Moon, G.D., Oh S., Jung, S.H., and Choi, Y.C., Effects of the fineness of limestone powder and cement on the hydration and strength development of PLC concrete. Constr Build Mater. 135, pp. 129-136, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.189 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.189
Mas, B., Cladera, A., and Bestard, J., Concrete with mixed recycled aggregates: influence of the type of cement. Constr Build Mater. 34, pp. 430-441, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.02.092 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.02.092
Abellán-García, J., y Pineda-Varón, A., Modelo predictivo de redes neuronales para estimar la resistencia a compresión de hormigones con materiales cementantes suplementarios y agregados reciclados, Matéria (Rio J.) 27(2), art. e13218, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-707620220002.1318 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-707620220002.1318
Çakir, O., Experimental analysis of properties of recycled coarse aggregate (RCA) concrete with mineral additives. Constr Build Mater. 68, pp. 17-25, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.06.032 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.06.032
Sobuz, M.H.R., Datta, S.D., Akid, A.S.M., et al. Evaluating the effects of recycled concrete aggregate size and concentration on properties of high-strength sustainable concrete. J King Saud Univ - Eng Sci. art. 004, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2022.04.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2022.04.004
Zheng, C., Lou, C., Du, G., Li, X., Liu, Z., and Li, L., Mechanical properties of recycled concrete with demolished waste concrete aggregate and clay brick aggregate. Results Phys. 9(April), pp. 1317-1322, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.04.061 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.04.061
Bravo, M., de Brito, J., Evangelista, L., and Pacheco, J., Superplasticizer’s efficiency on the mechanical properties of recycled aggregates concrete: Influence of recycled aggregates composition and incorporation ratio. Constr Build Mater. 153, pp. 129-138, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.07.103 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.07.103
Elsayed, M., Tayeh, B.A., Abu Aisheh, Y.I., El-Nasser, N.A., and Elmaaty, M.A., Shear strength of eco-friendly self-compacting concrete beams containing ground granulated blast furnace slag and fly ash as cement replacement. Case Stud Constr Mater. 17(July), art. 01354, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01354 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01354
Arul-Prakash, T.V., Natarajan, M., Senthil-Vadivel, T., and Karthik, V., Durability behavior of self compacting concrete made with recycled concrete aggregate. Int J Eng Technol. 7(35), art. 29139, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i3.35.29139 DOI: https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i3.35.29139
Zingg, A., Winnefeld, F., and Holzer, L., Interaction of polycarboxylate-based superplasticizers with cements containing different C3A amounts. CemConcr Compos. 31(3), pp. 153-162, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2009.01.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2009.01.005
Faella, C., Lima, C., Martinelli, E., Pepe, M., and Realfonso, R., Mechanical and durability performance of sustainable structural concretes: an experimental study. Cem Concr Compos. 71(August), pp. 85-96, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.05.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.05.009
Deng, X.H., Lu, Z.L., Li, P., and Xu, T., An investigation of mechanical properties of recycled coarse aggregate concrete. Arch Civ Eng. 62(4), pp.19-34, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/ace-2015-0107 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/ace-2015-0107
Kou, S.C., Poon, C.S., and Agrela, F., Comparisons of natural and recycled aggregate concretes prepared with the addition of different mineral admixtures. Cem Concr Compos. 33(8), pp. 788-795, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.05.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.05.009
Rashad, A.M., Metakaolin as cementitious material: history, scours, production and composition-A comprehensive overview. Constr Build Mater. 41, pp. 303-318, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.12.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.12.001
Poon, C.S., Lam, L., Kou, S.C., Wong, Y.L., Wong, R., Rate of pozzolanic reaction of metakaolin in high-performance cement pastes. Cement and Concrete Research, 31(9), pp. 1301-1306, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00581-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00581-6
Wild, S., Sabir, B.B., Bai, J., and Kinuthia, J., Self-compensating autogenous shrinkage in Portland cement—metakaolin—fly ash pastes. Adv Cem Res. 12(1), pp. 35-43, 2000. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/adcr.2000.12.1.35 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/adcr.2000.12.1.35
Brooks, J.J., and Johari, M.A., Effect of metakaolin on creep and shrinkage of concrete. Cem Concr Compos. (23), pp. 495-502, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(00)00095-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(00)00095-0
Arizzi, A., and Cultrone, G., Comparing the pozzolanic activity of aerial lime mortars made with metakaolin and fluid catalytic cracking catalyst residue: a petrographic and physical-mechanical study. Constr Build Mater. 184, pp. 382-390, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.002
Ferdosian, I., Camões, A., and Ribeiro, M., High-volume fly ash paste for developing ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). Cienc e Tecnol dos Mater. 29(1), e157-e161, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctmat.2016.10.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctmat.2016.10.001
Matias, D., De Brito, J., Rosa, A., and Pedro, D., Mechanical properties of concrete produced with recycled coarse aggregates - Influence of the use of superplasticizers. Constr Build Mater. 44, pp. 101-109, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.03.011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.03.011
Abellán-García, J., and García-Castaño, E., Development and research on Ultra-High-Performance concrete dosages in Colombia: a review. ACI Mater J., 119(3), pp. 209-221, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14359/51734617 DOI: https://doi.org/10.14359/51734617
Li, W., Xiao, J., Sun, Z., Kawashima, S., and Shah, S.P., Interfacial transition zones in recycled aggregate concrete with different mixing approaches. Constr Build Mater. 35, pp. 1045-1055, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.06.022 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.06.022
Cómo citar
IEEE
ACM
ACS
APA
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Descargar cita
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 DYNA

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
El autor o autores de un artículo aceptado para publicación en cualquiera de las revistas editadas por la facultad de Minas cederán la totalidad de los derechos patrimoniales a la Universidad Nacional de Colombia de manera gratuita, dentro de los cuáles se incluyen: el derecho a editar, publicar, reproducir y distribuir tanto en medios impresos como digitales, además de incluir en artículo en índices internacionales y/o bases de datos, de igual manera, se faculta a la editorial para utilizar las imágenes, tablas y/o cualquier material gráfico presentado en el artículo para el diseño de carátulas o posters de la misma revista.
















