Publicado
Machine learning in industrialization: a bibliometric analysis
Aprendizaje automático en la industrialización: un análisis bibliométrico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v92n235.115909Palabras clave:
machine learning, industrialization, bibliometrics, artificial intelligence, supervised learning, unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning (en)aprendizaje automático, industrialización, bibliometría, inteligencia artificial, aprendizaje supervisado, aprendizaje no supervisado, aprendizaje reforzado (es)
Descargas
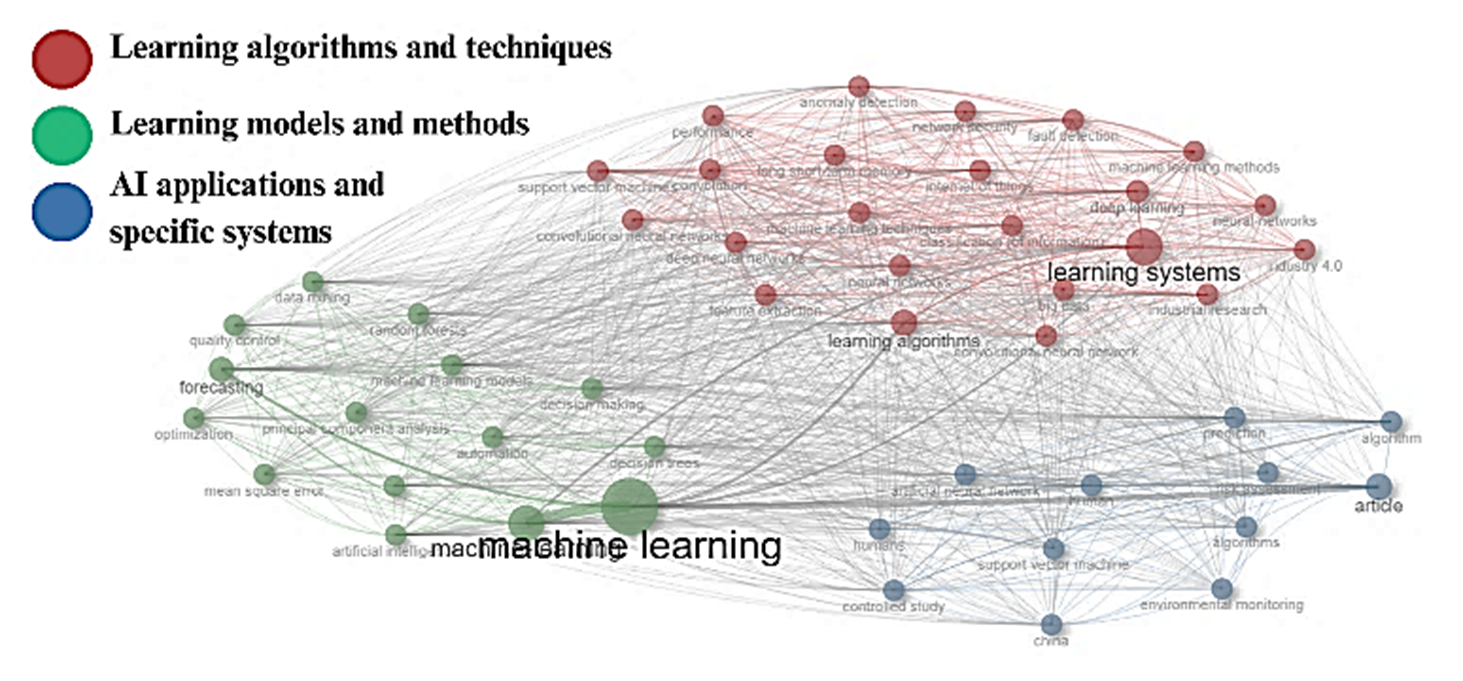
Machine learning is currently emerging as one of the most rapidly advancing technologies, with a recent upward trend in its use for process automation across industrial processes. The objective of this study was to conduct a bibliometric analysis to identify research trends in machine learning. The Scopus database was used to identify scientific production. Bibliometric indicators of visibility, impact, and concurrence were analyzed. The analysis of 7,335 documents, involving 22,383 authors, showed a growth rate of 20.86% from 1988 to early 2024. Three dominant research trends were identified: the first based on machine learning applications in industrial processes, the second referring to the human factor and artificial intelligence, and the third related to convolutional neural networks.
El machine learning es una de las tecnologías en auge actualmente, en los últimos años se ha observado una tendencia en su uso en la industria para la automatización de procesos. El objetivo de este estudio fue desarrollar un estudio bibliométrico para identificar las tendencias de investigación sobre machine learning en la industrialización. Se utilizó la base de datos Scopus para la identificación de la producción científica. Se analizaron indicadores bibliométricos de visibilidad, impacto y concurrencia. El análisis a partir de 7335 documentos, con la participación de 22383 autores, evidenció un crecimiento con una tasa de 20.86% en el intervalo de tiempo desde 1988 hasta inicios de 2024. Se identificaron tendencias dominantes al tema de investigación: la primera basada en la industria y el machine learning la segunda referida al factor humano y la inteligencia artificial, y la tercera relacionada con las redes neuronales convolucionales.
Referencias
[1] McGenity, C., Clarke, E.L., Jennings, C., Matthews, G., Cartlidge, C., Freduah-Agyemang, H., Stocken, D.D., and Treanor, D., Artificial intelligence in digital pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. NPJ Digit Med, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-024-01106-8
[2] Šuc, D., Vladušič, D., and Bratko, I., Qualitatively faithful quantitative prediction. Artif Intell, 158(2), pp.189–214, 2004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2004.05.002
[3] Ganjare, S.A., Satao, S.M., and Narwane, V., Systematic literature review of machine learning for manufacturing supply chain. TQM Journal, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-12-2022-0365
[4] Saleh, O., Otim, F.N., and Otim, O., Application of supervised learning classification modeling for predicting benthic sediment toxicity in the southern California bight: a test of concept. Science of the Total Environment, 901, art. 165946, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165946
[5] Kruglov, A.V., The unsupervised learning algorithm for detecting ellipsoid objects. Int J Mach Learn Comput, 9(3), pp.255–260, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18178/ijmlc.2019.9.3.795
[6] Keshavarz-Haddadha, P., Rezvani, M.H., Molla-Motalebi, M., and Shankar, A., Machine learning methods for service placement: a systematic review. Artif Intell Rev, 57(3), art. 10684-0, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10684-0
[7] Breque, M., De Nul, L., Petridis, A., Industry 5.0: towards a sustainable, human-centric and resilient European industry. Publications Office of the European Union, DOI: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2777/308407
[8] Shi, Y., Hu, J., Shang, D.T., Liu, Z., and Zhang, W., Industrialisation, Ecologicalisation and Digitalisation (IED): building a theoretical framework for sustainable development. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 123(4), pp. 1252-1277, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-06-2022-0371
[9] Wang, D., Hao, M., Li, N., and Jiang, D., Assessing the impact of armed conflict on the progress of achieving 17 sustainable development goals. IScience, 27(12), art. 111331, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.111331
[10] Ren, Y.M., Zhang, Y., Ding, Y., Wang, Y., and Christofides, P.D., Computational fluid dynamics-based in-situ sensor analytics of direct metal laser solidification process using machine learning. Comput Chem Eng, 143, art. 107069, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2020.107069
[11] Aria, M., and Cuccurullo, C., Bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetr, 11(4), pp. 959–75, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
[12] Adadi, A., and Berrada, M., Peeking inside the Black-Box: a survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access, 6, pp. 52138–60, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2870052
[13] Dwivedi, Y.K., Hughes, L., Ismagilova, E., et al, Artificial Intelligence (AI): multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int J Inf Manage, 57, art. 101994, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.08.002
[14] Yang, L., and Shami, A., On hyperparameter optimization of machine learning algorithms: theory and practice. Neurocomputing, 415, pp. 295–316, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.07.061
[15] Stamatatos, E., A survey of modern authorship attribution methods. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 60(3), pp. 538–56, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21001
[16] Qin, S.J., Survey on data-driven industrial process monitoring and diagnosis. Annu Rev Control, 36(2), pp. 220–34, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcontrol.2012.09.004
[17] Fuller, A., Fan, Z., Day, C., and Barlow, C., Digital Twin: Enabling technologies, challenges and open research. IEEE Access, 8, pp. 108952–108971, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2998358
[18] Blank, J., and Deb, K., Pymoo: multi-objective optimization in Python. IEEE Access, 8, pp. 89497–509, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990567
[19] Lu, Y., Huang, X., Dai, Y., Maharjan, S., and Zhang, Y., Blockchain and federated learning for privacy-preserved data sharing in industrial IoT. IEEE Trans Industr Inform, 16(6), pp. 4177–4186, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2019.2942190
[20] Wang, J., Ma, Y., Zhang, L., Gao, R.X., and Wu, D., Deep learning for smart manufacturing: methods and applications. J Manuf Syst, 48, pp. 144–156, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.01.003
[21] Zhang, W., Li, C., Peng, G., Chen, Y., and Zhang, Z., A deep convolutional neural network with new training methods for bearing fault diagnosis under noisy environment and different working load. Mech Syst Signal Process, 100, pp. 439–453, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.06.022
[22] Lee, K.M., Yoo, J., Kim, S.W., Lee, J.H., and Hong, J., Autonomic machine learning platform. Int J Inf Manage, 49, pp. 491–501, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.07.003
[23] Din, I.U., Guizani, M., Rodrigues, J.J.P.C., Hassan, S., and Korotaev, V.V., Machine learning in the internet of things: designed techniques for smart cities. Future Generation Computer Systems, 100, pp. 826–843, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.04.017
[24] Rajendran, D., Sasilatha, T., Rajendran, S., Selvaraj, S.K., Lacnjevac, C., Prabha, S.S., and Rathish, R.J., Application of machine learning in corrosion inhibition study. Materials Protection, 63(3), pp. 280–290, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5937/zasmat2203280R
[25] Alsina, E.F., Chica, M., Trawiński, K., and Regattieri, A., On the use of machine learning methods to predict component reliability from data-driven industrial case studies. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 94(5–8), pp. 2419–2433, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1039-x
[26] Yao, J., Tran, S.N., Sawyer, S., and Garg, S., Machine learning for leaf disease classification: data, techniques and applications. Artif Intell Rev, 56, pp. 3571–3616, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-023-10610-4
[27] Costa, M.A., Wullt, B., Norrlöf, M., and Gunnarsson, S., Failure detection in robotic arms using statistical modeling, machine learning and hybrid gradient boosting. Measurement (Lond), 146, pp. 425–436, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.06.039
[28] Peng, J., Muhammad, R., Wang, S.L., and Zhong, H.Z., How Machine Learning Accelerates the Development of Quantum Dots?†. Chin J Chem, 39(1), pp. 181–188, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202000393
[29] Siddesh-Padala, V., Gandhi, K., and Pushpalatha, D.V., Machine learning: the new language for applications. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence, 8(4), pp. 411–421, 2019. DOI: http://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v8.i4.pp411-421
[30] Morin, M., Gaudreault, J., Brotherton, E., Paradis, F., Rolland, A., Wery, J., and Laviolette, F., Machine learning-based models of sawmills for better wood allocation planning. Int J Prod Econ, 222, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.09.029
[31] Jaber, M.M., Ali, M.H., Abd, S.K., Jassim, M.M., Alkhayyat, A., Kadhim, E.H., Alkhuwaylidee, A.R., and Alyousif, S., AHI: a hybrid machine learning model for complex industrial information systems. J Comb Optim, 45(2), 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-023-00988-w
[32] Boutilier, J.J., and Chan, T.C.Y., Introducing and integrating machine learning in an operations research curriculum: an application-driven course. INFORMS Transactions on Education, 23(2), pp. 64–83, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1287/ited.2021.0256
[33] Guan, Z., Tian, H., Li, N., Long, J., Zhang, W., and Du, Y., High-accuracy reliability evaluation for the WC–Co-based cemented carbides assisted by machine learning. Ceram Int, 49(1), pp. 613–24, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.09.030
[34] Saxby, D.J., Killen, B.A., Pizzolato, C., Carty, C.P., Diamond, L.E., Modenese, L., Fernandez, J., Davico, G., Barzan, M., Lenton, G., da Luz, S.B., Suwarganda, E., Devaprakash, D., Korhonen, R.K., Alderson, J.A., Besier, T.F., Barrett, R.S., and Lloyd, D.G., Machine learning methods to support personalized neuromusculoskeletal modelling. Biomech Model Mechanobiol, 19(4), pp. 1169–1185, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-020-01367-8
[35] Kim, J., Kim, H., and Geum, Y., How to succeed in the market? Predicting startup success using a machine learning approach. Technol Forecast Soc Change, 193, art. 122614, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122614
[36] Greif, L., Röckel, F., Kimmig, A., and Ovtcharova, J., A systematic review of current AI techniques used in the context of the SDGs. Int J Environ Res, 19, art. 1, 2025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-024-00668-5
[37] Barua, A., Ahmed, M.U., and Begum, S., A Systematic literature review on multimodal machine learning: applications, challenges, Gaps and Future Directions. IEEE Access, pp. 14804–14831, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3243854
[38] Weinzierl, S., Zilker, S., Dunzer, S., and Matzner, M., Machine learning in business process management: a systematic literature review, 2024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124181
[39] Jiang, W., and Luo, J., Graph neural network for traffic forecasting: a survey. Expert Syst Appl, 207, art. 117921, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117921
[40] Jiang, W., Applications of deep learning in stock market prediction: Recent progress. Expert Syst Appl, 184, art. 115537, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115537
[41] Jiang, W. Graph-based deep learning for communication networks: a survey. Comput Commun, 185, pp. 40–54, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2021.12.015
[42] Purwono., Ma’arif, A., Rahmaniar, W., Fathurrahman, H.I.K., Frisky, A.Z.K., and Haq, Q.M.U., Understanding of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): a review. International Journal of Robotics and Control Systems, 2(4), pp. 739–748, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31763/ijrcs.v2i4.888
[43] Pérez-Cubero, E., and Poler, R., Aplicación de algoritmos de aprendizaje automático a la programación de órdenes de producción en talleres de trabajo: una revisión de la literatura reciente. Direccion y Organizacion, pp. 82–94, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.37610/dyo.v0i72.588
Cómo citar
IEEE
ACM
ACS
APA
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Descargar cita
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 DYNA

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
El autor o autores de un artículo aceptado para publicación en cualquiera de las revistas editadas por la facultad de Minas cederán la totalidad de los derechos patrimoniales a la Universidad Nacional de Colombia de manera gratuita, dentro de los cuáles se incluyen: el derecho a editar, publicar, reproducir y distribuir tanto en medios impresos como digitales, además de incluir en artículo en índices internacionales y/o bases de datos, de igual manera, se faculta a la editorial para utilizar las imágenes, tablas y/o cualquier material gráfico presentado en el artículo para el diseño de carátulas o posters de la misma revista.
















