Publicado
Development of a water level monitoring and control system for pumping stations in agricultural systems
Desarrollo de un sistema de monitoreo y control del nivel de agua para estaciones de bombeo en sistemas agrícolas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v92n237.117596Palabras clave:
agriculture, water management, limnigraph, ultrasonic sensor (en)agricultura, gestión del agua, limnígrafo, sensor ultrasónico (es)
Descargas
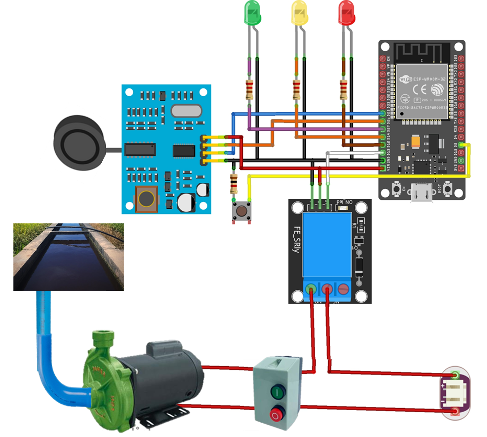
Monitoring water levels in reservoirs and suction pipes is essential to avoid failures in pumping and agricultural systems. This study aimed to develop an intelligent system for automated monitoring of water levels in irrigated agricultural reservoirs, ensuring safer operation of pumping stations and aiding decision-making. The system enables visualization, water level management, and protection of motor pumps. After assembly and programming, the prototype was installed in a reservoir. Tests showed a difference of less than 5 mm between manual and system measurements. Google Sheets was used for accurate data analysis. The control system includes a contactor, thermal relay, bipolar circuit breaker, simple control relay (activated by the ESP32), and two buttons — one normally closed and one normally open. The proposed intelligent system proved effective for automated water level management in reservoirs.
El monitoreo de los niveles de agua en los reservorios y tuberías de succión es esencial para evitar fallos en los sistemas de bombeo y en los sistemas agrícolas. Este estudio tuvo como objetivo desarrollar un sistema inteligente para el monitoreo automatizado de los niveles de agua en reservorios de riego agrícola, garantizando un funcionamiento más seguro de las estaciones de bombeo y apoyando la toma de decisiones. El sistema permite la visualización, gestión del nivel de agua y protección de las motobombas. Tras el montaje y la programación, el prototipo fue instalado en un reservorio. Las pruebas mostraron una diferencia de menos de 5 mm entre la medición manual y la realizada por el sistema. Se utilizó Google Sheets para el análisis preciso de los datos. El sistema de control incluye un contactor, relé térmico, disyuntor bipolar, relé de control simple (activado por el ESP32) y dos botones, uno normalmente cerrado y otro normalmente abierto. El sistema propuesto demostró ser eficaz para la gestión automatizada del nivel de agua en reservorios.
Referencias
[1] Pereira, L.-B., and Santos, M.-R., Dos desenvolvimento de um sistema Embarcado de Baixo Custo para Automatização do manejo de Irrigação Localizada, Revista Velho Chico, (2), pp. 50-56, 2022.
[2] Karami, M., McMorrow, G.-V., and Wang, L., Continuous monitoring of indoor environmental quality using an arduino-based data acquisition system, Journal of Building Engineering, (19), pp. 412-419, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2018.05.014.
[3] Chan, K., Schillereff, D.-N., Baas, A.-C.-W., Chadwick, M.-A., Main, B., Mulligan, M., O’Shea, F.-T., Pearce, R., Smith, T.-E.-L., van-Soesbergen, A., et al., Low-Cost Electronic Sensors for Environmental Research: pitfalls and Opportunities, prog. phys. Geogr., (45), pp. 305-338, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133320956567.
[4] Carvalho, A.-A., Medeiros, V.-W.-C., and de-Gonçalves, G.-E., Aplicação de sensores de baixo custo na estimativa da evapotranspiração potencial, Journal of Environmental analysis and progress, (6), pp. 119-127, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24221/jeap.6.2.2021.2843.119-127
[5] Castell, N., Dauge, F.-R., Schneider, P., Vogt, M., Lerner, U., Fishbain, B., Broday, D., and Bartonova, A., Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ Int, (99), pp. 293-302, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.007
[6] Reges, J.-P., Oliveira, F.-I., De-Sousa, J.-R., de-B., Carvalho, P.-C.-M., and Alexandria, A.-R., Development of a data Acquisition System for Photovoltaic systems, Revista Brasileira de Energia Solar, (10), pp. 77-87, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.59627/rbens.2019v10i2.281.
[7] Deng, Y., Wang, S., Bai, X., Wu, L., Cao, Y., Li, H., Wang, M., Li, C., Yang, Y., Hu, Z., et al., Comparison of soil moisture products from microwave remote sensing, land model, and reanalysis using global ground observations, Hydrol. Process (34), pp. 836-851, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13636
[8] De-Melo, D.-A., Silva, P.-C., da-Costa, A.-R., Delmond, J.-G., Ferreira, A.-F-.A., de Souza, J.-A., de Oliveira-Júnior, J.-F., da-Silva, J.-L-.B., da-Rosa, Ferraz-Jardim, A.-M., Giongo, P.-R., et al., Development and automation of a photovoltaic-powered soil moisture sensor for water management, Hydrology, (10), art. 80166, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10080166.
[9] Lino, D.-R., Lima-Neto, B.-P., de-Queiroz, L.-L., Feitosa, P.-B., Rodrigues, A.-A., and Santos-Teixeira, A., Dos irrigação automatizada com plataforma de desenvolvimento arduino na horta didática da Universidade Federal do Ceará, Irriga, (1), pp. 85-93, 2017. DOI: DOI: https://doi.org/10.15809/irriga.2017v1n1p85-93
[10] Campos, H., de-M., Oliveira, H.-F.-E., de-Mesquita, M., Castro, L.-E.-V., and de-Ferrarezi, R.-S., Low-Cost Open-source platform for irrigation automation. Comput, Electron. Agric., (190), art. 106481, 2021.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106481
[11] Kumar, V., Singh, C-D., Rao, K.-V.-R., Kumar, M., and Rajwade, Y.-A., Development of a Smart iot‐based drip irrigation system for precision farming. Irrigation and Drainage, (72), pp. 21-37, 2023.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2757
[12] Jia, W., Wei, Z., Tang, X., Zhang, Y., and Shen, A., Intelligent control technology and system of on-demand irrigation based on multiobjective optimization, Agronomy, (13), art. 13071907, 2023, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071907
[13] Lopes, I., Souza-Barbosa, R., Damascena-dos-Santos, D., and Medrado-de-Melo, J.-M., Melo-Vellame, L., Alves-de-Oliveira, E., Kramer-Schwiderke, S., LoRa-based iot platform for remote soil parameter monitoring. DYNA, 91(231), pp. 86-93, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v91n231.111612
[14] Goralski, M.-A., and Tan, T.-K., Artificial intelligence and sustainable development, International Journal of Management Education, (18), art. 100330, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.100330
[15] Silva, R.-J.-G., Sistema de automação do controle de volume de água em reservatório de abastecimento, Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso, Universidade Federal de Campina Grande, Campina Grande, Brasil, 2021.
[16] Yang, B., Wei, W., Chen, M., and Li, X.-N., Research on design of intelligent water-saving irrigation system based on Neural Network. Water Conserv, Tech. Supervis, (5), pp. 44-48, 2020.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAICA50127.2020.9181897
[17] Priya, O.-V., and Sudha, R., Impact of Internet of things (IoT) in smart agriculture. In: Advances in Parallel Computing, Rajesh, M., Vengatesan, K., Gnanasekar, M., Sitharthan R., Pawar, A.B., Kalvadekar, P.N., and Saiprasad, P., Eds., IOS Press BV, (39), pp. 40–47, 2021. ISBN 9781643682181
[18] Obaideen, K., Yousef, B.-A.-A., AlMallahi, M.-N., Tan, Y.-C., Mahmoud, M., Jaber, H., and Ramadan, M., An overview of smart irrigation systems using IoT, Energy Nexus, (7), art. 100124, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nexus.2022.100124
[19] Essamlali, I., Nhaila, H., and Khaili, M., El advances in machine learning and IoT for water quality monitoring: a comprehensive review, Heliyon, (10), art. 27920, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27920
[20] Wu, Z., Huang, Y., Huang, K., Yan, K., and Chen, H., A review of non-contact water level measurement based on computer vision and radar Technology. Water (Switzerland), (15), art. 183233, 2023, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183233
[21] Rocha, D.-P. de-A., Projeto formoso impactos socioeconômicos e ambientais no município de Bom Jesus da Lapa-BA, Codevasf, Brasília, 2023.
[22] Suresh, N., Hashiyana, V., Kulula, V.-P., and Thotappa, S., Smart water level monitoring system for farmers, 2019, pp. 213–228.
[23] Suresh, N., Hashiyana, V., Kulula, V.-P., and Thotappa, S., Smart water level monitoring system for farmers, IGI Global, (1), art. ch014, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-9246-4.ch014
[24] Pereira, T.-S.-R., de-Carvalho, T.-P., Mendes, T.-A., and Formiga, K.-T.-M., Evaluation of water level in flowing channels using ultrasonic sensors. Sustainability (Switzerland), (14), art. 14095512, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095512
[25] Andang, A., Hiron, N., Chobir, A., and Busaeri, N., Investigation of ultrasonic sensor type JSN-SRT04 performance as flood elevation detection. In: Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; Institute of Physics Publishing, art. 550, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/550/1/012018
[26] Khalina, T.-M., Eremochkin, S.-Y., art. Dorokhov, D.-V., The development of an energy efficient electric drive for agricultural machines. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater Sci., (1211), art. 012018, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/1211/1/012018
[27] Chowdury, M.-S.-U., Emran, T., Bin-Ghosh, S., Pathak, A., Alam, M.M., Absar, N., Andersson, K., and Hossain, M.-S, IoT based real-time river water quality monitoring system, Proceedings of the Procedia Computer Science, (155), 2019, pp. 161-168. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.08.025
[28] Mystkowski, A., and Kierdelewicz, A., Fractional-order water level control based on PLC: hardware-in-the-loop simulation and experimental validation. Energies (Basel), (11), art. 112928, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112928
[29] Santos, E.-M., Aplicação de plataformas de baixo custo na automação de processos industriais, Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Caruaru, Brasil, 2021.
[30] Zaragoza, M.-G., and Kim, H.-K., Comparative study of PLC and Arduino in automated irrigation system. International Journal of Control and Automation, (10), pp. 207-2018, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14257/ijca.2017.10.6.20
[31] Melo, D.-A. de-Silva, P.-C., Costa, A.-R. da-Delmond, J.-G., Ferreira, A.-F.-A., Souza, J.-A. de-Oliveira-Júnior, J.-F. de-Silva, J.-L.-B. da-Jardim, A.-M. da-R.F., Giongo, P.-R., et al., Development and automation of a photovoltaic-powered soil moisture sensor for water management, Hydrology, (10), art. 10080166, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10080166
Cómo citar
IEEE
ACM
ACS
APA
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Descargar cita
CrossRef Cited-by
1. Oleg IVANOV, Oleksii BURLAKA, Anton KELEMESH, Sergii LIASHENKO. (2025). MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE SYSTEM OF AUTOMATIC WATER LEVEL CONTROL OF THE HYDRAULIC PRESSURE RESERVOIR OF THE IRRIGATION SYSTEM. ENGINEERING ENERGY TRANSPORT AIC, , p.66. https://doi.org/10.37128/2520-6168-2025-3-7.
Dimensions
PlumX
Visitas a la página del resumen del artículo
Descargas
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 DYNA

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
El autor o autores de un artículo aceptado para publicación en cualquiera de las revistas editadas por la facultad de Minas cederán la totalidad de los derechos patrimoniales a la Universidad Nacional de Colombia de manera gratuita, dentro de los cuáles se incluyen: el derecho a editar, publicar, reproducir y distribuir tanto en medios impresos como digitales, además de incluir en artículo en índices internacionales y/o bases de datos, de igual manera, se faculta a la editorial para utilizar las imágenes, tablas y/o cualquier material gráfico presentado en el artículo para el diseño de carátulas o posters de la misma revista.
















