Published
Multicriteria decision-making analysis based methodology for predicting carbonate rocks' uniaxial compressive strength
Keywords:
Compressive strength, empirical equations, carbonate rock, analytical hierarchy. (en)ABSTRACT
Uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) deals with materials' to ability to withstand axially-directed pushing forces and especially considered to be rock materials' most important mechanical properties. However, the UCS test is an expensive, very time-consuming test to perform in the laboratory and requires high-quality core samples having regular geometry. Empirical equations were thus proposed for predicting UCS as a function of rocks' index properties. Analytical hierarchy process and multiple regression analysis based methodology were used (as opposed to traditional linear regression methods) on data-sets obtained from carbonate rocks in NE Turkey. Limestone samples ranging from Devonian to late Cretaceous ages were chosen; travertine-onyx samples were selected from morphological environments considering their surface environmental conditions Test results from experiments carried out on about 250 carbonate rock samples were used in deriving the model. While the hierarchy model focused on determining the most important index properties affecting on UCS, regression analysis established meaningful relationships between UCS and index properties; 0. 85 and 0. 83 positive coefficient correlations between the variables were determined by regression analysis. The methodology provided an appropriate alternative to quantitative estimation of UCS and avoided the need for tedious and time consuming laboratory testing
RESUMEN
La resistencia a la compresión uniaxial (RCU) trata con la capacidad de los materiales para soportar fuerzas empujantes dirigidas axialmente y, especialmente, es considerada ser uno de las más importantes propiedades mecánicas de los materiales rocosos. Sin embargo, una prueba de RCU es costosa, lleva mucho tiempo para hacerlo en el laboratorio y requiere muestras de núcleos de alta calidad que tienen una geometría regular.
Por lo tanto, ecuaciones empíricas fueron propuestas para la predicción de RCU como una función de las propiedades índice de las rocas. Las metodologías de proceso analítico jerárquico (PAJ) y análisis de regresión múltiple fueron utilizados (en vez de los métodos tradicionales de regresión lineal) en conjuntos de datos obtenidos de las rocas carbonatadas en el noreste de Turquía Muestras de rocas calizas que van desde el Devónico hasta finales del Cretácico fueron escogidas; muestras de travertino y ónix fueron seleccionadas de ambientes morfológicos teniendo en cuenta sus condiciones ambientales de superficie.
Los resultados de los experimentos llevados a cabo en alrededor de 250 muestras de rocas carbonatadas fueron utilizados para derivar un modelo Mientras que el modelo de jerarquía se centró en determinar las propiedades índice más importantes afectados por la RCU, el análisis de regresión establece relaciones significativas entre la RCU y las propiedades del índice; coeficientes de correlación positivas de 0,85 y 0,83 fueron determinadas por análisis de regresión entre las variables La metodología proporciona una alternativa adecuada para la estimación cuantitativa de la RCU y evita la necesidad de realizar pruebas del laboratorio las cuales son tediosas y dispendiosas
Multicriteria decision-making analysis based methodology for predicting carbonate rocks' uniaxial compressive strength
Hakan Ersoy and Derya Kanik
Karadeniz Technical University, Geological Engineering Department, 61080, Trabzon, Turkey, phone: + 90 462 377 35 06, fax: +90 462 325 7405 . E-mail: blavetirraa@hotmail.com; kanik@ktu.edu.tr
Record
Manuscript received: 06/02/2012
Accepted for publications: 01/06/2012
ABSTRACT
Uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) deals with materials' to ability to withstand axially-directed pushing forces and especially considered to be rock materials' most important mechanical properties. However, the UCS test is an expensive, very time-consuming test to perform in the laboratory and requires high-quality core samples having regular geometry. Empirical equations were thus proposed for predicting UCS as a function of rocks' index properties. Analytical hierarchy process and multiple regression analysis based methodology were used (as opposed to traditional linear regression methods) on data-sets obtained from carbonate rocks in NE Turkey. Limestone samples ranging from Devonian to late Cretaceous ages were chosen; travertine-onyx samples were selected from morphological environments considering their surface environmental conditions Test results from experiments carried out on about 250 carbonate rock samples were used in deriving the model. While the hierarchy model focused on determining the most important index properties affecting on UCS, regression analysis established meaningful relationships between UCS and index properties; 0. 85 and 0. 83 positive coefficient correlations between the variables were determined by regression analysis. The methodology provided an appropriate alternative to quantitative estimation of UCS and avoided the need for tedious and time consuming laboratory testing
Keywords: Compressive strength, empirical equations, carbonate rock, analytical hierarchy.
RESUMEN
La resistencia a la compresión uniaxial (RCU) trata con la capacidad de los materiales para soportar fuerzas empujantes dirigidas axialmente y, especialmente, es considerada ser uno de las más importantes propiedades mecánicas de los materiales rocosos. Sin embargo, una prueba de RCU es costosa, lleva mucho tiempo para hacerlo en el laboratorio y requiere muestras de núcleos de alta calidad que tienen una geometría regular.
Por lo tanto, ecuaciones empíricas fueron propuestas para la predicción de RCU como una función de las propiedades índice de las rocas. Las metodologías de proceso analítico jerárquico (PAJ) y análisis de regresión múltiple fueron utilizados (en vez de los métodos tradicionales de regresión lineal) en conjuntos de datos obtenidos de las rocas carbonatadas en el noreste de Turquía Muestras de rocas calizas que van desde el Devónico hasta finales del Cretácico fueron escogidas; muestras de travertino y ónix fueron seleccionadas de ambientes morfológicos teniendo en cuenta sus condiciones ambientales de superficie.
Los resultados de los experimentos llevados a cabo en alrededor de 250 muestras de rocas carbonatadas fueron utilizados para derivar un modelo Mientras que el modelo de jerarquía se centró en determinar las propiedades índice más importantes afectados por la RCU, el análisis de regresión establece relaciones significativas entre la RCU y las propiedades del índice; coeficientes de correlación positivas de 0,85 y 0,83 fueron determinadas por análisis de regresión entre las variables La metodología proporciona una alternativa adecuada para la estimación cuantitativa de la RCU y evita la necesidad de realizar pruebas del laboratorio las cuales son tediosas y dispendiosas
Palabras claves: Resistencia a la compresión, ecuaciones empíricas, rocas carbonatadas, jerarquía analítica
Introduction
Intact rocks' uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) is the main parameter used for almost all rock mechanical studies in most civil, geological and mining projects (Bieniawski 1974; Cargill and Shakoor 1990); however, regular geometry, high-quality core samples are necessary for determining UCS Standard cores cannot always be extracted from weak, highly-fractured, thinly-bedded, foliated rocks. This test is thus expensive, time-consuming and requires well-prepared rock samples Resent trends in estimating UCS from simple laboratory index tests has been improved to overcome such difficulties, and simple prediction models have become attractive for engineering geologists using non-destructive and easily-applied techniques such as rocks' ultrasonic wave velocity (UWV) and index properties. Many attempts have been made to predict intact rocks' UCS (Kahraman 2001; Katz et al., 2000; Koncagul and Santi 1999; Chau and Wong 1996). Some researchers have found that sound velocity is closely related to rock properties (Gaviglio 1989; Chang et al., 2006; Yalçinalp et al., 2008; Babacan et al., 2009; Moradian and Behnia, 2009) whilst other have correlated UCS with index properties such as porosity, density and UWV (Ramana and Venkatanarayana 1973; Yasar and Erdogan 2004; Kanik 2010)
Simple statistical methods-based multiple regression techniques have been used to establish predictive models; new techniques such as artificial neural networks and fuzzy inference systems have been used for developing predictive models for estimating the required parameters during recent years (Grima and Babuska 1999; Kayabasi et al., 2002, Gokceoglu and Zorlu 2004; Sonmez et al., 2003; Karakus and Tutmez 2006; Dehghan et al., 2010, Yagiz et al., 2011) . Different evaluation methods have been developed to establish predictive models; such methods include linear vector approach, matrix method, fuzzy set theory, checklist methods, parametric ranking methods and multi criteria decision analysis based methodologies Analytic hierarchy process (AHP), was developed as a type of multi-criteria analysis, to standardise multi-criteria decision-making (Saaty 1980) However, AHP uses a quantitative comparison method based on pair-wise comparisons of decision-making criteria, rather than utility and weighting functions Many engineering geological projects have adopted such as approach (Cook et al., 1984; Siddiqui et al., 1996; Ersoy and Bulut 2009)
The paper presents multi-criteria decision-making and multiple regression analysis-based methodology for predicting UCS regarding carbonate rocks' index properties. The model is based on non-destructive and relatively easy to apply laboratory tests
Research methodology
Sampling location and geology
The morphology of mountainous region being studied in north-eastern Turkey (Figure 1) consist of rough, irregular land having steep slopes and peaks reflecting the eastern Black Sea region's geology and tectonic features. The main morphological units (mainly faults and folds) have been shaped by structural elements in the region trending NE-SW. The region is drained by the Harsit and Çoruh rivers, forming the most significant fluvial system. Deep incision forms like v-shaped valleys are characterised by deep gorges and steep slopes in these drainage systems
Turkey is located in the Alpine-Himalayan orogenic belt having the world's richest natural stone formations; it is the country having 5 billion tons of reserves and almost 35% of the world's natural stone reserves.
The eastern Black Sea region has rich potential in terms of the variety of carbonate- bearing rocks. The region has around 450 million tons natural stone reserves almost 70% of production today consists of travertine and limestone, the remaining 30% being volcanic rocks. The rock samples for this study were collected from 5000 km2 in the southern zone of the eastern Pontides (NE Turkey). The Eastern Pontide Belt is a major metal-logenetic province in the eastern Black Sea coastal region and forms a 500 km long and 100 km wide mountain chain along the Black Sea coast The Eastern Pontides may be subdivided into northern and eastern zones on structural and lithological differences (Ozsayar et al., 1981; Okay and Sahinturk 1997) . The northern zone is dominated by Late Cretaceous and Middle Eocene volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks, whereas pre-Late Cretaceous sedimentary rocks are widely exposed in the Southern Zone (Arslan et al., 1997; Eyuboglu 2006; Sen 2007) (Figure 2).
The limestone samples were selected from pre-Late Cretaceous platform carbonates which are widely exposed in the area and Liassic-aged formations; travertine and onyx samples were selected from the Gümüçhane, Bayburt and Giresun area. Three rock types from ten rock formations were sampled and tested for this study Table 1 gives the rock type, age, location and description of the samples
UWV, unit weight, water absorption and content are the rock materials' most important index properties and they are often related to porosity. Porosity is the ratio of the non-solid volume to the total volume of material and it also describes how densely the material is packed In the study, firstly unit weight, water content, apparent porosity and water absorption by weight were determined with respect to the description criteria of ISRM (1981) A Pundit Plus ultra-sonic pulse (USP) instrument giving more precise rock sample measurements and two 54 KHz transducers having piezoelectric properties were used in this study to calculate ultrasonic longitudinal wave velocity. The transducers were located parallel to the surface of the sample, transit time was measured and ultrasonic wave velocities were calculated from transit time
UCS was determined for the study according to ISRM (1981) description criteria. Core surface flatness was supplied for the UCS test to obtain an even load distribution; specimens were loaded axially up to failure
Establishing decision-making methods
Regression analysis includes any techniques for modelling and analysing several variables when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables (Freedman 2005). Multiple regression is aimed at learning more about the relationship between several independent or predictable variables and a dependent or criterion (Davis 1986) Regression analysis was used in this with analytic hierarchy process (AHP), a widely accepted decision making method Constraints are compared to each other in AHP, to designate each variable's relative importance in accomplishing an overall goal Numerical values were assigned to each pair of constraints using established guidelines and a constrained matrix is built. The sum of each column within the matrix was then normalised and weighting was calculated Mathematic formulation (simple additive weighting) was defined following an equation for calculating final grading values in multiple criteria problems (Saaty 1980);

where, v(y) was area's suitability index, w was a criterion's weighting or importance factor of a, y was a criterion's degree or compliance level, i was the criterion number and q was the number of criteria.
Pairwise comparisons were used to determine each criterion's relative importance; AHP is based on such approach Decision makers can quantify their opinions about the criteria magnitude by using a verbal scale when comparing pairs of criteria. The pairwise comparison matrix (PCM) constructed by decision-makers in the previous had to have the following attributes;

The next step was to calculate the criteria's relative importance weighting implied by previous comparisons Saaty (1980) proposed estimating PCM's right principal eigenvector which can be approximated using the geometric mean for each row of the PCM (by multiplying the elements in each row and then taking the nth root, where n is the number of criteria) This mode is known as multiplicative AHP (Saaty and Millet 2000) and was used in the present work. The calculated geometric means were then normalised and relative importance weighting extracted
Integrating site selection criteria was based on multi-criteria assessment methods (Eastmen, 1995):

where, Sk was the land's suitability for landfill for objective k (priority groups), (fi)k was factor i (discriminating features) for objective k, (wi)k was the weighting for factor i (score given experimental studies) for objective k, (rj)k was constraint j for objective k (value 0 or 1), S was multi-objective suitability and wk was the weighting for objective k
Results
The rocks' index and strength properties
UCS is an expensive and very time-consuming test. The core surfaces have to be ground down to make them parallel at a specified tolerance and a high load capacity loading frame is usually required. Thus, in the study, ten groups of carbonate rock samples were collected in the Southern Zone of the eastern Pontides (NE Turkey) to establish some relationships between UCS and index properties
In the study the index and strength properties of the rocks were determined in accordance with ISRM (1981). The results of the laboratory studies are given Table 2 and Table 3 When taking into consideration the mean values of the water content, water absorption by weight, apparent porosity, P wave velocity and UCS value data, the highest values were observed for Erzincan limestone and the lowest values were observed for Gümüshane travertines However, the values of the UCS were obtained between 20 and 66 MPa for travertines, 20 and 70 MPa for onyx and 25 and 162 for different limestones. Depending on the mineral shapes, weathering features and occurrence of the microcracks, the UCS values varied in a wide range as found in the study.
Empirical relationship between index and strength properties
Rock materials' uniaxial compressive strength greatly depends on their index properties such as porosity, water content, water absorption and mineral composition P wave velocity and porosity are the most preferred properties for predicting UCS amongst such properties (Sachpazis 1990; Tugrul and Zarif 1999; Palchik 1999).
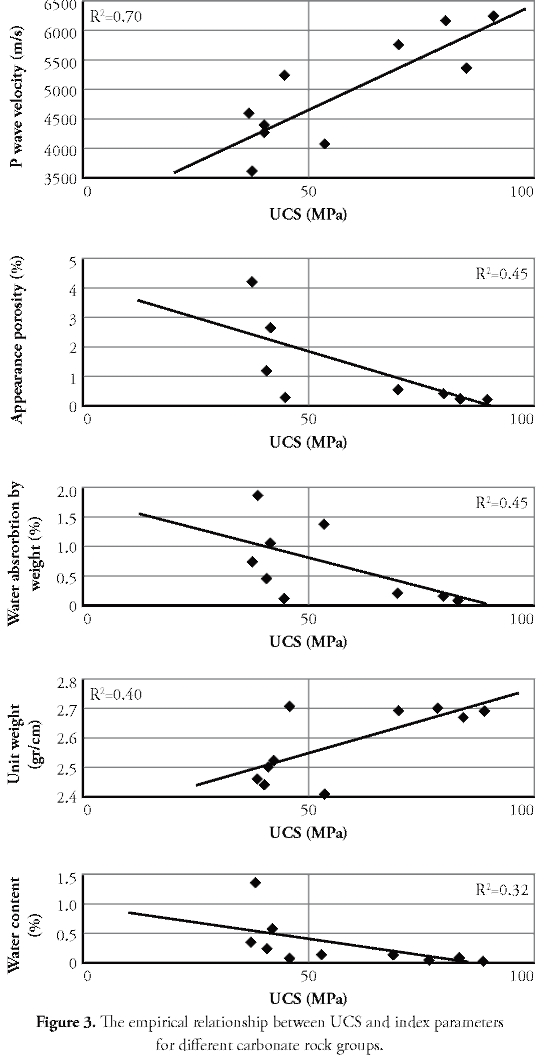
Regression analysis is usually preferred for establishing statistical relationships between different variables. Relationship intensity of between variables is defined by regression values and correlation coefficients; explanatory variables must thus be weighted regarding dependent variables before multiple regression analysis to establish an empirical model. AHP used the data obtained from linear regression analysis results concerning ten rock groups (Table 1 and Figure 3) to decide which material properties should be selected as explanatory variables from rock materials' index properties.
This represents a tool which reduces time and the cost involved in many engineering models. Table 4 lists the priority vectors for all criteria; relative importance weightings are included in the final column of this table. AHP parameters are also shown in the table, indicating that the judgments (and therefore final relative importance weightings) seemed to be reasonable. The method needed a scale of numbers indicating how many times more important or dominant one element was over another element regarding the criterion or property to which they were being compared. The AHP analysis showed that the most important criteria affecting on UCS for the carbonate rocks being studied were UWV (45% weighting) and apparent porosity (33 % weighting). The other index properties' weighting did not surpase %10.
As regression analysis provides a means of summarising the relationship between variables, multiple regression analysis-based methodology was used to establish some numerical relationships between rock materials' ultrasonic wave velocity, apparent porosity and UCS Furthermore it is known that Vp decreases with increased porosity Vp and n-1 were thus used in the equations for predicting UCS in this study. Index properties were considered to be explanatory variables, and the UCS a depending variable Figure 4 and 5 show multiple regression analysis results, involving some positive correlations between UWV rate regarding apparent porosity and UCS: such relationships were characterised by 0.71 and 0. 87 regression coefficients. However, Figure 6 indicates meaningful empirical relationships for all travertines and limestones and the relationships are represented by the formulas given in Table 5
A goodness of fit test establishes whether an observed frequency distribution differs from a theoretical distribution; however, a model's suitability is tested using the difference between observed and expected values. Normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution which is often used as a first approach for describing real-valued random variables tending to cluster around a single mean value A normal distribution would thus be expected in the histograms showing difference between observed and expected values. Line-scatter plot diagrams of observed-expected values (Figure 7a and c) and histograms of difference between observed and expected values (Figure 7b and d) were prepared and normal distributions were observed Histograms having a normal distribution showed that these equations did fairly well in estimating UCS using Vp/n. The results showed that the model being tested was suitable for the study
Conclusions
This study involved three types of carbonate rocks being collected from ten rock formations in the north-eastern Turkey Laboratory studies were conducted in line with ISRM (1980) to establish some relationships between P wave velocity, apparent porosity and UCS and AHP-based multiple regression analyses methodology was used for statistically analyzing the suggested methods and results AHP analysis indicated that UWV (45% weighting) and apparent porosity (33% weighting) were the most important index properties affecting on UCS regarding the carbonate-bearing rocks being studied Multiple regression analysis correlations indicated by the 0. 81-0. 87 regression coefficient were determined for UWV rate regarding apparent porosity and UCS. The equations obtained by such analysis results were practical, simple and accurate enough to apply and may be recommended for use in practice
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by the Karadeniz Technical University Scientific Research Fund. (Project No: 2008.112. 005.10). The authors would like to thank Bülent Yalçinalp and Ali Babacan from Karadeniz Technical University in Trabzon (Turkey) for field and laboratory work. The authors would also like to thank Nazmiye Yazici from Güvencem Marble Limited Company for helping during all stages of the study
References
Arslan, M., Tuysuz, N., Korkmaz, S., Kurt, H. (1997). Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the eastern Pontide volcanic rocks, Northeast Turkey Chemie der Erde, 57: 157-187
Babacan, A. E., Ersoy, H., Gelisli, K. (2009). Determination of physical and mechanic properties of rocks with direct and indirect methods: A case study on the beige limestones in the Eastern Pontides, Proceedings of the 21st International Mining Congress and Exhibition of Turkey, Antalya, 123-130
Bieniawski, Z. T. (1974). Estimating the strength of rock materials. Journal of the South African Institute Mining Metallurgy, 74: 312-320
Cargill, J S , Shakoor, A (1990) Evaluation of empirical methods for measuring the uniaxial compressive strength International Journal of Rock Mechanic and Mining Science, 27: 495-503
Chang, C , Mark, D , Zoback, A , Abbas, K B (2006) Empirical relations between rock strength and physical properties in sedimentary rocks Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 51: 223-237
Chau, K T , Wong, R H C (1996) Uniaxial compressive strength and point load strength International Journal of Rock Mechanic and Mining Science, 33: 183-188
Cook, T., Falchi, P, Mariano, R. (1984). An urban allocation model combining time series and analytic hierarchical methods Management Science, 30 (2): 198-208
Davis, J C (1986) Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology John Wiley and Sons, New York
Dehghan, S., Sattari, G. H., Chelgani, C., Aliabadi, M. (2010). Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength and modulus of elasticity for travertine samples using regression and artificial neural networks. Mining Science and Technology, 20: 41-46
Ersoy, H , Bulut, F (2009) Spatial and multi-criteria decision analysis-based methodology for landfill site selection in growing urban regions Waste Management and Research, 27(5):489-500
Eyuboglu, Y. (2006). Description and Geotectonic Important of the Alaskan-Type Ma c-Ultrama c Rocks in the Eastern Pontide Magmatic Arc (NE Turkey), PhD Thesis, Karadeniz Technical University, Trabzon, Turkey (unpublihed)
Freedman, D (2005) Statistical models theory and practice London: Cambridge University Press
Gaviglio, P (1989) Longitudinal waves propagation in a limestone: the relationship between velocity and density Rock Mechanic and Rock Engineering, 22: 299-306
Gokceoglu, C , Zorlu, K (2004) A fuzzy model to predict the uniaxial compressive strength and the modulus of elasticity of a problematic rock. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligent, 17(1): 61-72
Grima, A.M., Babuska, R. (1999). Fuzzy model for the prediction of un-confined compressive strength of rock samples. International Journal of Rock Mechanic and Mining Science, 22: 339-349
ISRM (International Society for Rock Mechanics) suggested methods: rock characterization, testing and monitoring E T Brown (ed ), Pergamon Press, London; 1981
Kahraman, S (2001) Evaluation of simple methods for assessing the uniaxial compressive strength of rock International Journal of Rock Mechanic and Mining Science, 38: 981-994
Kanik, D (2010) Predicting of uniaxial compressive strength of carbonate rocks using simple test methods Karadeniz Technical University Natural Sciences Institute Master thesis, Turkey (unpublished)
Karakus, M , Tutmez, B (2006) Fuzzy and multiple regressions modelling for evaluation of intact rock strength based on point load, schmidt hammer and sonic velocity Rock Mechanic and Rock Engineering, 39(1): 45-57
Katz, O., Reches, Z., Roegiers, J. C. (2000). Evaluation of mechanical rock properties using a schmidt hammer International Journal of Rock Mechanic and Mining Science, 37(4): 723-728
Kayabasi, A , Gokceoglu, C , Ercanoglu, M (2002) Estimating the deformation modulus of rock masses: a comparative study International Journal of Rock Mechanic and Mining Science, 40: 55-63
Koncagul, C. E., Santi, P. M. (1999). Predicting the unconfined compressive strength of the Breathitt shale using slake durability, shore hardness and rock structural properties International Journal of Rock Mechanic and Mining Science, 36: 139-153
Moradian, Z A , Behnia, M (2009) Predicting the uniaxial compressive strength and static young's modulus of intact sedimentary rocks using the ultrasonic test ASCE International Journal of Geomechanics, 9(1): 14-19
Okay, A. I, Sahinturk, O. (1997). Geology of the eastern Pontides. In: Robinson AG (ed), regional and Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea and Surrounding Region, American Association of Petroleum Geologist (AAPG) Memoir, 68: 291-311
Ozsayar, T , Pelin, S , Gedikoglu, A (1981) Cretaceous in the eastern Pontides, Karadeniz Technical University Journal of Earth Sciences, 1: 65-74 (in Turkish with English abstract)
Palchik, V. (1999). Influence of porosity and elastic modulus on uniaxial compressive strength in soft brittle porous sandstones Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 32: 303-309
Ramana, Y V , Venkatanarayana , B (1973) Laboratory studies on Kolar rocks International Journal of Rock Mechanic and Mining Science, 10: 465-489
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Saaty, T., Millet, I. (2000). On the relativity of relative measures accommodating both rank preservation and rank reversals in the AHP European Journal of Operational Research, 121: 205-212
Sachpazis, C I (1990) Correlating Schmidt hardness with compressive strength and young's modulus of carbonate rocks Bulletin International Association of Engineering Geology, 42: 75-83
Siddiqui, M.Z., Everett, J.W., Vieux, B.E. (1996). Landfill siting using geographic information systems: a demonstration Journal of Environmental Engineering, 122: 515-523
Sonmez, H , Gokceoglu, C , Ulusay, R (2003) An application of fuzzy sets to the geological strength index (GSI) system used in rock engineering. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligent, 16(3): 251-269
Sen, C (2007) Jurassic volcanism in the eastern Pontides Turkish Journal of Earth Sciences, 16: 523-539
Yalçinalp, B., Ersoy, H., Firat Ersoy, A. (2008). Geological and geotechnical properties of Bahcecik (Gümüshane, NE Turkey) travertines. Journal of Earth Science, 32: 24-36 (in Turkish with English abstract)
Tugrul, A , Zarif, I H (1999) Correlation of mineralogical and textural characteristics with engineering properties of selected granitic rocks from Turkey. Engineering Geology, 51: 303-317.
Yagiz, S., Sezer, E.A., Gokceoglu, C. (2011). Artificial neural networks and nonlinear regression techniques to assess the influence of slake durability cycles on the prediction of uniaxial compressive strength and modulus of elasticity for carbonate rocks, International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, DOI: 10.1002/nag.1066
Yasar, E., Erdogan, Y. (2004). Estimation of rock physicomechanical properties using hardness methods Engineering Geology, 71: 281-288
How to Cite
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Download Citation
Article abstract page views
Downloads
License
Earth Sciences Research Journal holds a Creative Commons Attribution license.
You are free to:
Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.