Published
Marco de referencia para el modelamiento y simulación de la ciberdefensa marítima - MARCIM: estado del arte y metodología
Framework for modeling and simulation of maritime cyberdefense - MARCIM: state of the art and methodology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v91n231.109774Keywords:
ciberdefensa; cibernética; ciberseguridad; defensa; informática; marítimo; modelo de simulación (es)ciberdefense; cybernetics; cybersecurity; defense; informatics; maritime; simulation models (en)
Downloads
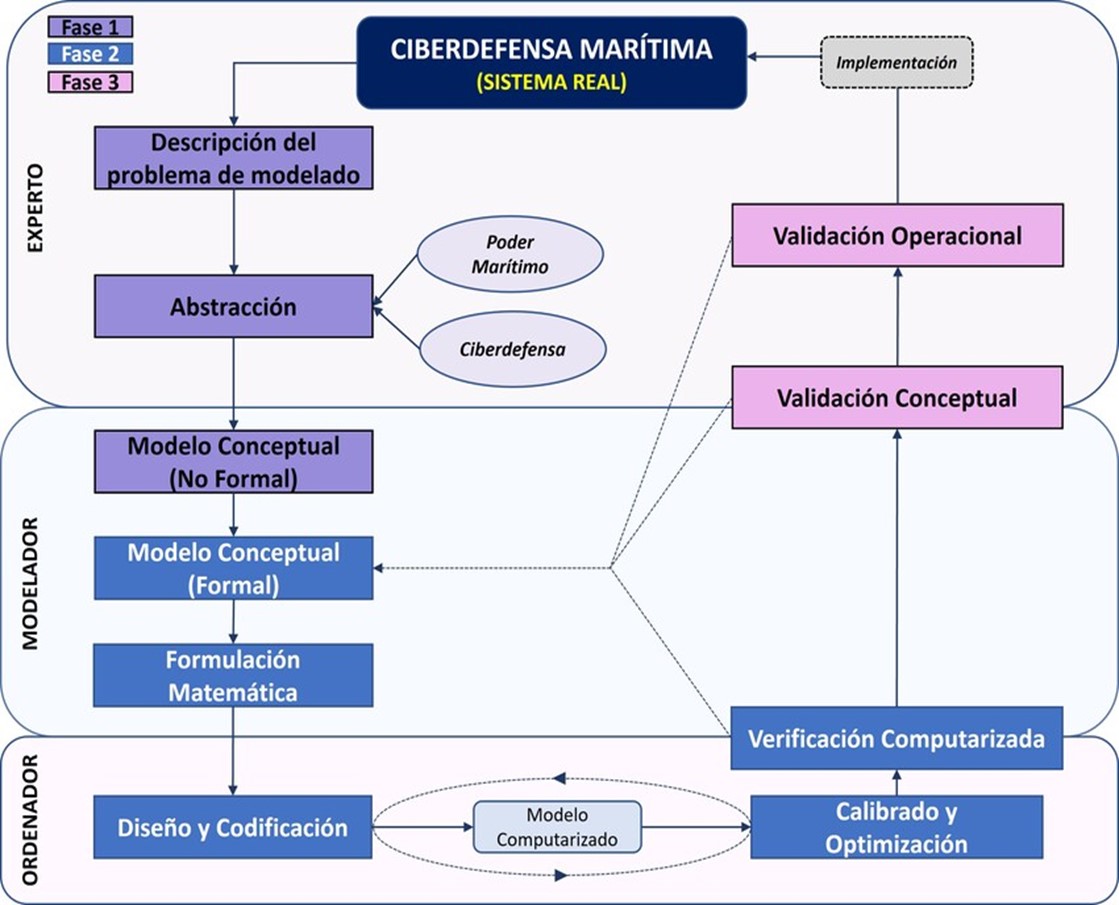
El artículo presenta el estado del arte y metodología del proyecto de investigación doctoral “Marco de referencia para el modelamiento y simulación de la ciberdefensa marítima – MARCIM”. El estado del arte definió los antecedentes del problema de investigación, estado de la actividad científica, tendencias y retos de las temáticas del MARCIM: ciberdefensa, modelamiento y simulación en ciberseguridad y ciberdefensa; y ciberseguridad y ciberdefensa marítima. La metodología se planteó con un enfoque en modelamiento de sistemas complejos, por fases y actores de aplicación. El artículo concluye principalmente que la ciberdefensa marítima a nivel estratégico se comporta como un sistema complejo, con dinámicas, procesos y elementos que no se pueden identificar claramente, que requieren del modelamiento y simulación, con un enfoque metaheurístico, para estudiar el conjunto de acciones e interacciones entre sus entidades.
The article presents the state of the art and methodology of the doctoral research project "Framework for modeling and simulation of maritime cyberdefense - MARCIM". The state of the art defined the background of the research problem, the state of scientific activity, trends and challenges related to MARCIM: cyberdefense, modeling and simulation in cyber security and cyberdefense; and maritime cybersecurity and cyberdefense. The methodology was established with a focus on modeling complex systems, by phases and application actors. The article mainly concludes that maritime cyberdefense at a strategic level behaves like a complex system, with dynamics, processes and elements that cannot be clearly identified, which require modeling and simulation, with a metaheuristic approach, to study the set of actions and interactions between its entities.
References
Cabuya-Padilla, D.E., Framework for modeling and simulation of maritime cyberdefense at strategic level – MARCIM. Doctoral Thesis. Escuela Naval de Cadetes “Almirante Padilla”, Cartagena, Colombia, 2021.
Armada República de Colombia. Plan de Desarrollo Naval 2042. Jefatura de Planeación Naval, Dirección de Planeación Estratégica, editors. ARC; [en línea]. Bogotá, Colombia, 2020, 135 P. Disponible en: https://www.escuelanaval.edu.co/es/file-download/download/public/14011
Departamento Nacional de Planeación. Documento CONPES 3854 - Política Nacional de Seguridad Digital. Consejo Nacional de Política Económica y Social. [en línea]. BogotáColombia, 2017. Disponible en: https://colaboracion.dnp.gov.co/CDT/Conpes/Económicos/3854.pdf
Valencia-Arias, A., Patiño-Toro, O., Arenas-Fernández, A., Garcés-Giraldo, L.F., Umba-López, A.M. y Benjumea-Arias, M.L., Tendencias investigativas en el estudio de la ciberdefensa: un análisis bibliométrico. RISTI - Rev Iber Sist e Tecnol Inf - RISTI. [en línea]. (E29), pp. 366–379, 2020. Disponible en: http://www.risti.xyz/issues/ristie29.pdf
Shukla, G., and Gochhait, S., Cyber security trend analysis using Web of Science: a bibliometric analysis. Eur J Mol Clin Med. 7(6), pp. 2567–76, 2020.
Sabillon, R., Cavaller, V., and Cano, J., National cyber security strategies: global trends in Cyberspace. Int J Comput Sci Softw Eng [en línea]. 5(5), pp. 67–81, 2016. [cited: 2020, Aug 17th]. Available at: http://www.IJCSSE.org
Baezner, M., and Cordey, S., National Cybersecurity strategies in comparison-challenges for Switzerland Center for Security Studies (CSS). ETH Zürich, [online]. 2019, 33 P., Available at: http://www.css.ethz.ch
North Atlantic Council. NATO Modelling and Simulation Master Plan. Rome, Italy, 2012, pp. 1-10.
Izaguirre-Olmedo, J., Vista de análisis de los ciberataques realizados en América Latina. INNOVA Research Journal, 3(9), pp. 172–181, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.33890/innova.v3.n9.2018.837 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33890/innova.v3.n9.2018.837
Cornaglia, S. y Vercelli, A.H., La ciberdefensa y su regulación legal en Argentina (2006-2015). URVIO - Rev Latinoam Estud Segur. (20), pp. 46-62, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17141/urvio.20.2017.2601 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17141/urvio.20.2017.2601
Departamento Nacional de Planeación. Documento CONPES 3995 - Política Nacional de Confianza y Seguridad Digital, [en línea]. Consejo Nacional de Política Económica y Social, Bogotá, Colombia, 2020. [cited: 2020, Aug 11th]. Disponible en: https://colaboracion.dnp.gov.co/CDT/Conpes/Económicos/3995.pdf
International Telecommunication Union. Global cybersecurity index. Measuring the digital transformation. [online]. 2020. Available at: https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/str/D-STR-GCI.01-2021-PDF-S.pdf
Organización de los Estados Americanos. Hacia una estrategia nacional de ciberseguridad. México D.F., 2017.
Espinosa, E.I., Hacia una estrategia nacional de ciberseguridad en México. Rev Adm Pública [online]. L(1), pp. 115–146, 2015. [cited: 2020, Aug 18th], Available at: https://revistas-colaboracion.juridicas.unam.mx/index.php/rev-administracion-publica/article/view/19862/17821
Junta Interamericana de Defensa. Informe II Conferencia de Ciberdefensa, [en línea]. Washington, USA, 2020. [cited: 2021, Apr. 14th]. Disponible en: https://www.iadfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Ciberdefensa10.pdf
Ganuza, N., Guía de ciberdefensa: orientaciones para el diseño, planeamiento, implantación y desarrollo de una ciberdefensa militar. Washington, USA, 2020.
Conferencia de las Naciones Unidas sobre Comercio y Desarrollo - UNCTAD. Review of Maritime Transport 2020. United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. [online]. New York, USA. 2020. Available at: https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/rmt2020_en.pdf
Alcaide, J.I., and Llave, R.G., Critical infrastructures cybersecurity and the maritime sector. Transportation Research Procedia, 45, pp. 547-554, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2020.03.058 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2020.03.058
Hellenic Shipping News Worlwide. Maritime cyber attacks increase by 900% in three years. In: International Shipping News, Piracy and Security News [online]. 2020. [cited: 2021, May 26th]. Available at: https://www.marineinsight.com/shipping-news/maritime-cyber-attacks-increase-by-900-in-three-years/#
Cabuya-Padilla, D.E., Alvarado-Carvajal, C.F., Carrascal-Ortiz, R.A., Riola-Rodríguez, J.M., Fajardo-Toro, C.H. y Escandon-Bernal, S.P., Ciberseguridad y ciberdefensa marítima: análisis bibliométrico años 1990 – 2021. RISTI - Rev Iber Sist e Tecnol Inf., 49, pp. 197-210, 2022.
Mraković, I., and Vojinović, R.. Maritime cyber security analysis – How to reduce threats? Trans Marit Sci., 8(1), pp. 132–139, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7225/toms.v08.n01.013
Armada República de Colombia. Portafolio de I+D+i de la Armada de Colombia [en línea]. Bogotá, 2021. Disponible en: https://minciencias.gov.co/sites/default/files/upload/convocatoria/anexo_4._alcance_tematicas_de_las_propuestas.pdf
MinCiencias. Programa Nacional en Seguridad y Defensa. Minciencias. [en línea]. 2013 [cited: 2022, Feb 13th]. Disponible en: https://minciencias.gov.co/node/1130
Elsevier. Scopus [online]. 2023 [cited: 2023, Jan 4th]. Available at: https://www.scopus.com/home.uri?zone=header&origin=
CRAN Project. The Comprehensive R Archive Network [online]. 2020. [cited: 2021, Aug 6th]. Available at: https://cran.r-project.org/
K-Synth Srl. Bibliometrix [online]. 2023. [cited: 2023, Jan 4th]. Available at: https://www.bibliometrix.org/home/
Llerena-Paz, M.A. y Arévalo-Avecillas, M.E., Indicadores bibliométricos: origen, definición y aplicaciones científicas en el ecuadorR. Espíritu Emprend TES, [en línea]. 5(1), pp. 130–53, 2021. [cited: 2021, Mar 7]. Disponible en: https://www.scimagojr.com/ DOI: https://doi.org/10.33970/eetes.v5.n1.2021.253
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., and Lim, W.M., How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. [en línea]. 133(March), pp. 285–296, 2021. Disponible en: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Ávila-Toscano, J.H., Cienciometría y bibliometría. El estudio de la producción científica. Métodos, enfoques y aplicaciones en el estudio de las Ciencias Sociales, 2018, 316 P.
Villalobos-Álvarez, J.M., Análisis bibliométrico años 2000-2021: modelamiento y simulación en ciberseguridad y ciberdefensa. Rev Derrotero. 15(Seguridad y Defenssa), pp. 77–102, 2021.
Kotenko, I., Agent-Based modeling and simulation of cyber-warfare between malefactors and security agents in Internet. In: Simulation in Wider Europe - 19th European Conference on Modelling and Simulation, ECMS 2005. St. Petersburg, 2005, pp.33-43.
Kotenko, I., Multi-agent modelling and simulation of cyber-attacks and cyber-defense for homeland security. In: 2007 4th IEEE Workshop on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications, IDAACS. St. Petersburg, 2007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/IDAACS.2007.4488494
Dobson, G.B., and Carley, K.M., Cyber-FIT: an agent-based modelling approach to simulating cyber warfare. In: Lee, D., Lin, YR., Osgood, N., and Thomson, R., Eds., Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Modeling. SBP-BRiMS 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 10354. Springer, Cham. 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-60240-0_18 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-60240-0_18
Wilensky, U., NetLogo, [online]. 2016. [cited: 2021, Jul 13th]. Available at: https://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/
Tam, K., and Jones, K., MaCRA: a model-based framework for maritime cyber-risk assessment. WMU J Marit Aff [online]. 18(1), pp. 129–63, 2019. [cited: 2020, Oct 14th]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13437-019-00162-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13437-019-00162-2
Katina, P.F., Tolk, A., Keating, C.B., and Joiner, K.F., Modelling and Simulation in complex system governance. Int J Syst Syst Eng. 10(3), pp. 262–92, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSSE.2020.109739
Shiva, S., Roy, S., and Dasgupta, D., Game theory for cyber security. In: CSIIRW ’10: Proceedings of the Sixth Annual Workshop on Cyber Security and Information Intelligence Research. [online]. Oak Ridge, TN. 2010, pp. 1–4. [cited 2020 Aug 1]. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228676698%0D
Bradshaw, J.M., Carvalho, M., Bunch, L., Eskridge, T., Feltovich, P.J., Johnson, M., et al., Sol: An Agent-Based Framework for Cyber Situation Awareness. KI - Künstliche Intelligenz, 26(2), pp. 127-140, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13218-012-0179-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13218-012-0179-2
Pastrana, S., Tapiador, J.E., Orfila, A., and Peris-Lopez, P., DEFIDNET: a framework for optimal allocation of cyberdefenses in intrusion detection Networks. Comput Networks. 80, pp. 66–88, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2015.01.012 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2015.01.012
Bodeau, D.J., Mccollum, C.D., and Fox, D.B., Cyber wargaming: framework for enhancing cyber wargaming with realistic business context [online]. Mc Lean, Virginia, USA, 2018. Available at: http://www.mitre.org/HSSEDI
Katsantonis, N.M., Kotini, I., Fouliras, P., and Mavridis, I., Conceptual framework for developing cyber security serious games. In: IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference, EDUCON. IEEE Computer Society, 2019, pp. 872–81. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/EDUCON.2019.8725061
Norman, M.D., and Koehler, M.T.K., Cyber defense as a complex adaptive system: a model-based approach to strategic policy design. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference of The Computational Social Science Society of the Americas, 2017, pp. 1-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3145574.3145595
Liu, S.Z., Li, Y.F., and Yang, Z., Modelling of cyber-attacks and defenses in local metering system. Energy Procedia. 145, pp. 421–426, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.04.069 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.04.069
Boyu, G.,and Libao, S., Modeling an attack-mitigation dynamic game-theoretic scheme for security vulnerability analysis in a cyber-physical power system. IEEE Access, 20, art. 2973030, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2973030 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2973030
Hasan, S., Dubey, A., Karsai, G., and Koutsoukos, X., A game-theoretic approach for power systems defense against dynamic cyber-attacks. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst. 115, art. 105432, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2019.105432 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2019.105432
Zeng, W., and Germanos, V., Modelling hybrid cyber kill chain, [online]. 2019. [cited: 2020. Oct 14th]. Available at: https://www.lockheedmartin.com
Maathuis, C., Pieters, W., and Van den Berg, J., Decision support model for effects estimation and proportionality assessment for targeting in cyber operations. Defence Technology, 17(2), pp. 352-374, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2020.04.007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2020.04.007
Jacq, O., Brosset, D., Kermarrec, Y., and Simonin, J., Cyber-attacks real time detection: towards a cyber situational awareness for naval systems. In: Cyber SA 2019: International Conference on Cyber Situational Awareness, Data Analytics and Assessment, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CyberSA.2019.8899351 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CyberSA.2019.8899351
Pitropakis, N., Logothetis, M., Andrienko, G., Stefanatos, J., Karapistoli, E., and Lambrinoudakis, C., Towards the creation of a threat intelligence framework for maritime infrastructures. In: Katsikas, S., et al. Computer Security. CyberICPS SECPRE SPOSE ADIoT 2019 2019 2019 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11980. Springer, Cham., 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42048-2_4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42048-2_4
Caselles-Moncho, A., Modelización y simulación de sistemas complejos. Tesis de grado, Universidad de Valencia, Valencia, España, 2008, 134 P.
Izquierdo, L., Galan, J., Santos, J. y Del Olmo, R., Modelado de sistemas complejos mediante simulacion basada en agentes y dinámica de sistemas. Empiria Rev Metodol Ciencias Soc. 16, pp. 85–112, 2008. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5944/empiria.16.2008.1391
Siegfried, R., Modeling and simulation of complex systems. Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, München, 2014, 233, P. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-07529-3
Sargent, R.G., Verification and validation of simulation models. In: Proceedings of the 2011 Winter Simulation Conference, 2011, pp. 83-98. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/WSC.2010.5679166 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/WSC.2011.6147750
Cabuya-Padilla, D.E., and Castaneda-Marroquin, C., Maritime cyberdefense actors taxonomy for command and control. In: Smart Innovation Systems and Technologies. United Kingdom, 2022, pp. 37-46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4884-7_4
Alba-Rocha, D.A., Ortegon-Vega, J.R., Cabuya-Padilla, D.E., Riola-Rodríguez, J.M. y Fajardo-Toro, C.H., Modelo conceptual del sistema del poder marítimo a nivel estratégico en Colombia. RISTI - Rev Iber Sist e Tecnol Inf. 49, pp. 211–221, 2022.
Buffa, B.A, Métodos matemáticos para modelos basados en agentes. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Córdoba, Argentina, 2015, 39 P.
Schervish, M.J., Review of Simulation Modeling and Analysis., by Law, A.M., and Kelton, W.D., Journal of the American Statistical Association, 78(383), pp. 743–744, 1983. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/2288169 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/2288169
Abar, S., Theodoropoulos, G.K., Lemarinier, P., and O’Hare, G.M.P., Agent based modelling and simulation tools: a review of the state-of-art software. Computer Science Review. 24, pp. 13-33, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2017.03.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2017.03.001
Python Software Foundation. Python [online]. 2023. Available at: https://www.python.org/
Weiner, M.G., War Gaming Methodology [online]. 1959. [cited: 2020, Sep 18th]. Available at: https://www.rand.org/content/dam/rand/pubs/research_memoranda/2008/RM2413.pdf
Burns, S., Della-Volpe, D., Babb, R., Miller, N., and Muir, G., War Gamers’ Handbook - A guide for professional war gamers. War Gaming Department, U.S. Naval War College, 2013.
Maldonado, C.E., Gómez-Cruz, N.A., Modelamiento y simulación de sistemas complejos. Universidad del Rosario; Bogotá, Colombia, pp. 1-32, 2010.
How to Cite
IEEE
ACM
ACS
APA
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Download Citation
License
Copyright (c) 2024 DYNA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The author of a paper accepted for publication in any of the journals published by the School of Mines will yield all the property to the National University of Colombia rights free of charge, within which include article: the right to edit, publish, reproduce and distribute both print and digital media, as well as including in an article in international indexes and / or databases, likewise, it enables the publisher to use images, tables and/or graphic material presented in Article for designing covers or posters of the magazine. By assuming the economic rights of the article, it may be reproduced partially or totally in any printed or digital media without express permission of the same.















