Published
Analysis, Modeling, and Simulation Solution of Induced-Draft Fan Rotor with Excessive Vibration: A Case Study
Solución de análisis, modelado y simulación de rotor de ventilador de tiro inducido con vibración excesiva: un caso de estudio
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15446/ing.investig.111284Keywords:
Monitoring and data analysis, fault diagnosis, computer simulation, mitigate mechanical vibrations (en)Monitoreo y análisis de datos, diagnóstico de fallas, simulación por computadora, mitigar vibraciones mecánicas (es)
Downloads
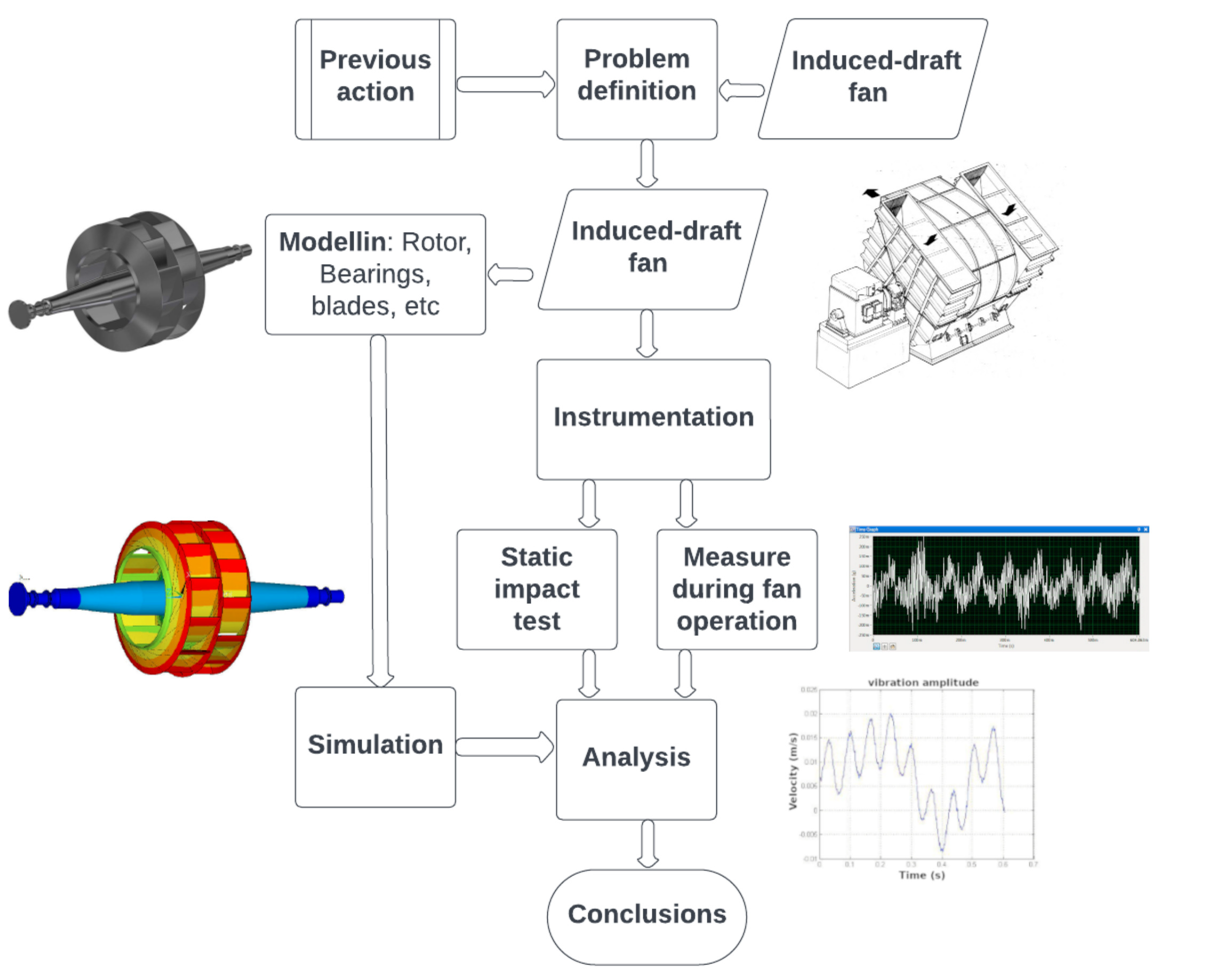
In the modern industry, computer modeling and simulation tools have become fundamental to estimating the behavior of rotodynamic systems. These computational tools allow analyzing possible modifications as well as alternative solutions to changes in design, with the aim of improving performance. Nowadays, rotodynamic systems, present in various industrial applications, require greater efficiency and reliability. Although there are deep learning methodologies for monitoring and diagnosing failures which improve these standards, the main challenge is the lack of databases for learning, a problem that can be addressed through experimental monitoring and computer analysis. This work analyzes the vibrations of two induced-draft fans with excess vibration in a thermoelectric plant in Mexico. A vibration analysis was carried out through the instrumentation and monitoring of accelerometers located at crucial points in the fans. The results of this experimental analysis were validated by computer simulation based on FEM. The results show that the operating speed of the induced-draft fans is very close to their natural frequency, causing considerable stress and potential failures due to excessive vibration. Finally, this work presents a practical solution to modify the natural frequency of induced-draft fans, so that they can function correctly at the required operating speed, thus mitigating excessive vibration issues.
En la industria moderna, las herramientas de modelado y simulación computacional se han vuelto fundamentales para estimar el comportamiento de los sistemas rotodinámicos. Estas herramientas computacionales permiten analizar posibles modificaciones y soluciones alternativas a cambios en el diseño, con el objetivo de mejorar el rendimiento. Hoy en día, los sistemas rotodinámicos, presentes en diversas aplicaciones industriales, requieren mayor eficiencia y fiabilidad. Aunque existen metodologías de aprendizaje profundo para el monitoreo y diagnóstico de fallas que mejoran estos estándares, el principal desafío es la falta de bases de datos para el aprendizaje. Este problema puede ser abordado a través del monitoreo experimental y el análisis computacional. Este trabajo analiza las vibraciones de dos ventiladores de tiro inducido con exceso de vibración en una planta termoeléctrica en México. Se realizó un análisis de vibración a través de la instrumentación y el monitoreo de acelerómetros ubicados en puntos cruciales de los ventiladores. Los resultados de este análisis experimental fueron validados por simulación computacional basada en el método de elementos finitos. Los resultados muestran que la velocidad de operación de los ventiladores de tiro inducido está muy cerca de su frecuencia natural, causando un estrés considerable y posibles fallas debido a la vibración excesiva. Finalmente, este trabajo presenta una solución práctica para modificar la frecuencia natural de los ventiladores de tiro inducido, de modo que puedan funcionar correctamente a la velocidad de operación requerida, mitigando así los problemas de vibración excesiva.
References
Benchekroun, M. T., Zaki, S., Hezzem, B., & Laacha, H. (2023). Kiln process fan vibrations prediction based on machine learning models: Application to the raw mill fan. Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum, volume 6, 6.https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2023006006
Benrahmoune, M., Ahmed, H., Mouloud, G., & XiaoQi, C.(2018). Detection and modeling vibrational behavior of a gas turbine based on dynamic neural networks approach. Strojnícky časopis-Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 68(3), 143–166. https://doi.org/10.2478/scjme-2018-0032
Blanco-Ortega, A., Beltrán-Carbajal, F., Silva-Navarro, G., & Méndez-Azúa, H. (2010). Control de vibraciones en maquinaria rotatoria. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e Informática Industrial RIAI, 7(4), 36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1697-7912(10)70058-3
Chapagain, A. & Silwal, B. (2023). Influence of rotor eccentricity on large synchronous generator. RESSD 2023 International Conference on Role of Energy for Sustainable Social Development, 1–4.
Čorović, S. & Miljavec, D. (2020). Modal analysis and rotordynamics of an interior permanent magnet synchronous motor: An experimental and theoretical study. Applied Sciences, 10(17), 5881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10175881
Cui, L., Wang, X., Xu, Y., Jiang, H., & Zhou, J. (2019). A novel switching unscented kalman filter method for remaining useful life prediction of rolling bearing. Measurement, 135, 678–684. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.12.028
Dhamande, L. S., Bhaurkar, V. P., & Patil, P. N. (2023). Vibration analysis of induced draught fan: A case study. Materials Today: Proceedings, 72, 657–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.08.329
Dhiya, F., R., M. B., & A., Y. H. (2023). Interferómetro machzehnder recubierto de óxido de grafeno basado en sensor de gas de amoníaco. Nexo Revista Científica, 36(06), 1132–1140. https://doi.org/10.5377/nexo.v36i06.17469
Di, H., Chen, Z., Tao, Y., & Gang, C. (2022). An intelligent anomaly detection method for rotating machinery based on vibration vectors. IEEE Sensors Journal, 22(14), 14294–14305. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2022.3179740
Donolo, P., Bossio, G., De Angelo, C., García, G., & Donolo, M. (2016). Voltage unbalance and harmonic distortion effects on induction motor power, torque and vibrations. Electric Power Systems Research, 140, 866–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2016.04.018
Doshi, S., Katoch, A., Suresh, A., Razak, F. A., Datta, S., Madhavan, S., Zanhar, C., & Gundabattini, E. (2021). A review on vibrations in various turbomachines such as fans, compressors, turbines and pumps. Journal of Vibration Engineering and Technologies, 9(7), 1557–1575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-021-00313-x
Guo, R., Zhang, G., Zhang, Q., Zhou, L., Yu, H., Lei, M., & Lv, Y. (2021). An adaptive early fault detection model of induced draft fans based on multivariate state estimation technique. Energies, 14(16), 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164787
Jagtap, H. P., Bewoor, A. K., & Kumar, R. (2020). Failure analysis of induced draft fan used in a thermal power plant using coordinated condition monitoring approach: A case study. Engineering Failure Analysis, 111, 104442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104442
Jerzy, C., Przemyslaw, M., & Piotr, O. (2014). Tests of rotary machines vibrations in steady and unsteady states on the basis of large diameter centrifugal fans. Eksploatacja i Niezawodnos´c´ , 16(2), 211–216.
Jesús, T., Liline-Daniel, C.-H., Alejandra, A. P., José-Joel, G.-B., & Juan-B, H.-R. (2024). Vibrations of a violin while the f-holes were sequentially cut. Acoustics Australia, 52(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40857-024-00313-3
Jorgen, W. L., Elie, B. A., Cheng, H. S., W., P. C., & Coda, H. (1965). Rotor Bearings Dynamic Design Technology, Part III:: desing handbook for fluid film type bearings (1 ed.). Mechanical Technology Inc.
Kalmár-Nagy, T., Bak, B. D., Benedek, T., & Vad, J. (2015). Vibration and noise of an axial flow fan. Periodica Polytechnica Mechanical Engineering, 59(3), 109–113. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPme.7948
Kaneko, Y., Kawashita, R., & Kanki, H. (2022).8 -steam turbine rotor design and rotor dynamics analysis. Advances in Steam Turbines for Modern Power Plants (Second Edition), Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy, 163–194. Woodhead Publishing, (second edition ed.). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-824359-6.00011-1
Li, P., Pang, L., & Lin, Z. (2020). Vibration fault diagnosis and dynamic balance processing analysis of blower in thermal power plant. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, volume 467, 012110. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/467/1/012110
Liu, R., Yang, B., Zio, E., & Chen, X. (2018). Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: A review. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 108, 33–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.02.016
Lu, H., Pavan Nemani, V., Barzegar, V., Allen, C., Hu, C., Laflamme, S., Sarkar, S., & Zimmerman, A. T. (2023). A physics-informed feature weighting method for bearing fault diagnostics. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 191, 110171. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2023.110171
M, J. & K, P. (2023). Matlab-based fault diagnosis of industrial rotor-bearing systems. Insight-Non-Destructive Testing and Condition Monitoring, 65(5), 278–283. https://doi.org/10.1784/insi.2023.65.5.278
Manish, D., Kumar, J. S., Vikas, S., Kumar, S. S., & Dhirendra, A. (2015). Fatigue (FEA) and modal analysis of a centrifugal fan. International Journal of Recent advances in Mechanical Engineering (IJMECH), 4(2), 77–91. https://doi.org/10.14810/ijmech.2015.4209
Mohamad, T. H., Abbasi, A., Kappaganthu, K., & Nataraj, C. (2023). On extraction, ranking and selection of data-driven and physics-informed features for bearing fault diagnostics. Knowledge-Based Systems, 276, 110744. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110744
Ni, Q., Ji, J., Halkon, B., Feng, K., & Nandi, A. K. (2023). Physics-informed residual network (piresnet) for rolling element bearing fault diagnostics. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 200, 110544. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2023.110544
Niko, L., Jari, P., & Esa, P. (2011). The effect of foundation on fan vibration response. Journal of Structural Mechanics, 44(1), 1–20.
Noureddine, A. & Noureddine, M. (2022). Computational investigation of vibration characteristics analysis for industrial rotor. Acta Mechanica et Automatica, 16(4). https://doi.org/10.2478/ama-2022-0044
Novotnỳ, P., Hrabovskỳ, J., Juračka, J., Klíma, J., & Hort, V. (2019). Effective thrust bearing model for simulations of transient rotor dynamics. International journal of mechanical sciences, 157, 374–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.04.057
Pingchao, Y., Dayi, Z., Yanhong, M., & Jie, H. (2018). Dynamic modeling and vibration characteristics analysis of the aero-engine dual-rotor system with fan blade out. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 106, 158– 175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.12.012
Qingjie, Z., Guangxiang, L., You, X., & Chengyu, Z. (2020). Torsional vibration analysis of shaft in an induced draft fan due to variable frequency drive. IEEE Access, 8, 174723–174735. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3026325
Ren, G.-P., Zhang, H.-T., Wu, Y., & Ding, H. (2023). A general double-input synchronous signal processor for imbalanced vibration mitigation in amb-rotor systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 53, 3823–3832. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2022.3232517
Shabaneh, N. & Zu, J. W. (2003). Nonlinear dynamic analysis of a rotor shaft system with viscoelastically supported bearings. J. Vib. Acoust., 125(3), 290–298. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1547684
Tarek, K., Nouredine, O., & Abderrazek, D. (2018). Experimental vibratory analysis of a fan motor in industrial environment. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 98(9-12), 2439– 2447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2391-1
Trebuna, F., Simcák, F., Bocko, J., Hunady, R., & Pástor, M. (2014). Complex approach to the vibrodiagnostic analysis of excessive vibration of the exhaust fan. Engineering Failure Analysis, 37, 86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2013.11.015
Wang, Z., Chen, Y., Ouyang, H., & Wang, A. (2020). Investigation of vibration characteristics of titanium widechord fan blade. Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies, 8, 529–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-019-00108-1
Wei, W., Lv, Y., Liu, Y., Li, Q., Xu, S., & Li, J. (2022). An early fault detection method of the induced draft fan based on long-short term memory network and double warning thresholds. 2022 34th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), 5262–5267. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCDC55256.2022.10033743
Xiangyang, D., Shiqiang, C., Zhenlin, L., Zhulong, Z., & Yihan, C. (2023). Experimental study on fan aerodynamic noise variation characteristics under non-proportional variation law. Sustainability, 15(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032025
Xie, Z., Yang, K., He, T., & Jiao, J. (2023). Experimental and theoretical analysis on the nonlinear rotor-dynamic performances and vibration characteristics of a novel bearing-rotor system. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 199, 110416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2023.110416
Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zeng, J., Ma, H., Yang, Y., & Cao, D. (2024). Insight on uncertainty of geometrically nonlinear rotor with rub-impact under maneuvering motion. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2023.118018
Yu-Ling, H., Ling, T., Kai, S., Wen-Hao, Z., Xue-Wei, W., & Hai-Peng, W. (2023). Impact of static air-gap eccentricity fault on synchronous generator efficiency. Energies, 16(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/en16073294
Zenglin, G. & Gordon, K. R. (2003). Instability boundary for rotor-hydrodynamic bearing systems, part 1: Jeffcott rotor with external damping. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 125(4), 417–422. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1547466
How to Cite
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Download Citation
CrossRef Cited-by
1. Tian Xie, Qiusheng Zhang, Haiping Chen, Ning He, Heng Zhang, Haitao Zhu. (2025). Automatic monitoring of induced draft fans of coal-fired units based on a PCLA model. Measurement Science and Technology, 36(10), p.106213. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6501/ae1313.
2. Mădălin Andreica, Angela Maria Andreica. (2025). Vibration-induced failures in industrial ventilation systems: A predictive maintenance approach. Journal of Vibration and Control, https://doi.org/10.1177/10775463251366352.
Dimensions
PlumX
Article abstract page views
Downloads
License
Copyright (c) 2024 José-Joel González-Barbosa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors or holders of the copyright for each article hereby confer exclusive, limited and free authorization on the Universidad Nacional de Colombia's journal Ingeniería e Investigación concerning the aforementioned article which, once it has been evaluated and approved, will be submitted for publication, in line with the following items:
1. The version which has been corrected according to the evaluators' suggestions will be remitted and it will be made clear whether the aforementioned article is an unedited document regarding which the rights to be authorized are held and total responsibility will be assumed by the authors for the content of the work being submitted to Ingeniería e Investigación, the Universidad Nacional de Colombia and third-parties;
2. The authorization conferred on the journal will come into force from the date on which it is included in the respective volume and issue of Ingeniería e Investigación in the Open Journal Systems and on the journal's main page (https://revistas.unal.edu.co/index.php/ingeinv), as well as in different databases and indices in which the publication is indexed;
3. The authors authorize the Universidad Nacional de Colombia's journal Ingeniería e Investigación to publish the document in whatever required format (printed, digital, electronic or whatsoever known or yet to be discovered form) and authorize Ingeniería e Investigación to include the work in any indices and/or search engines deemed necessary for promoting its diffusion;
4. The authors accept that such authorization is given free of charge and they, therefore, waive any right to receive remuneration from the publication, distribution, public communication and any use whatsoever referred to in the terms of this authorization.


























